Unit 4 – Carbohydrates
4.2 Categories of Carbohydrates
We’ll begin our discussion of carbohydrates by getting acquainted with the structure of different types of carbohydrates, food sources of each and how carbohydrates are made.
First, all carbohydrates are composed of the same chemical elements:
- carbon (that’s the “carbo-” part)
- hydrogen and oxygen, in about a two-to-one proportion, just like in H2O (that’s the “-hydrate” part)
For this reason, you may see carbohydrates abbreviated as “CHO” in, or “carbs” for short.
Carbohydrates can be divided into two main types: simple and complex. Simple carbohydrates are composed of just one or two sugar units, whereas complex carbohydrates contain many sugar units. Figure 4.4 is an overview of the types of carbohydrates.
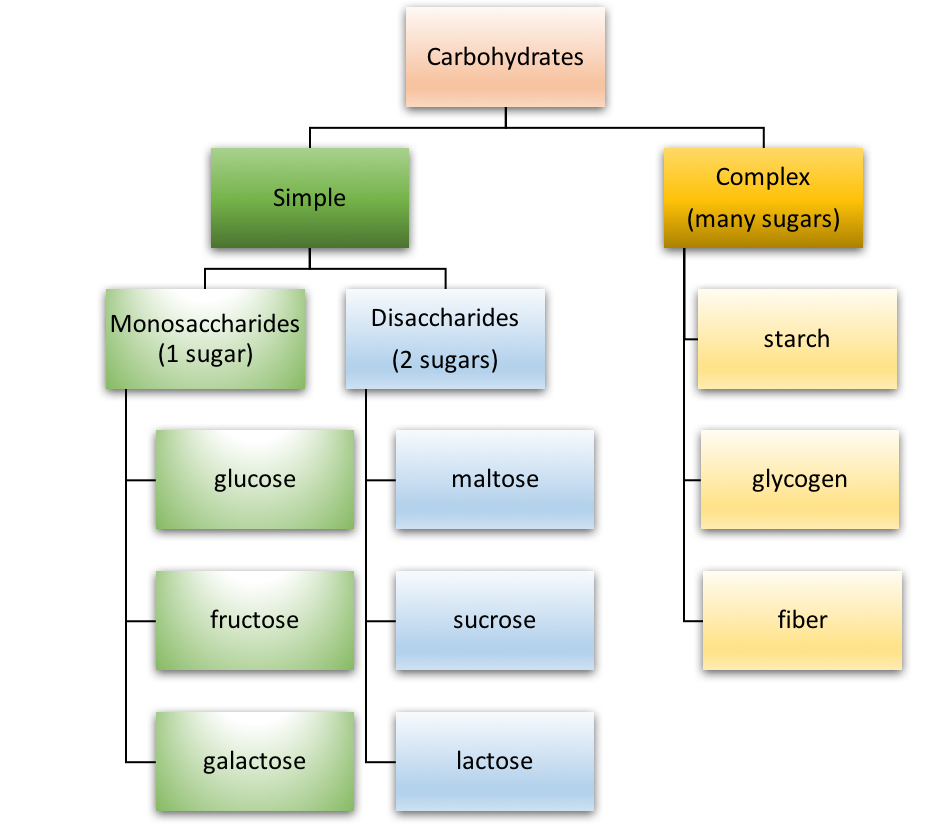
Simple carbohydrates
Simple carbohydrates are sometimes called “sugars” or “simple sugars.” There are two types of simple carbohydrates: monosaccharides and disaccharides.
Monosaccharides contain one sugar unit, so they’re the smallest of the carbohydrates. (The prefix “mono-” means “one.”) The small size of monosaccharides gives them a special role in digestion and metabolism. Food carbohydrates must be broken down to monosaccharides before they can be absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, and they also circulate in blood in monosaccharide form.
The Monosaccharides: Glucose, Fructose, and Galactose
All three monosaccharides have the same chemical formula (C6H12O6); the atoms are just arranged a bit differently.
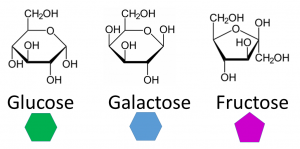
1 – Glucose
In humans, glucose is one of the most important nutrients for fueling the body. It’s especially important for the brain, which isn’t very good at using other fuel sources. Muscles, on the other hand, can use fat as an energy source. (Muscles use a combination of fat and glucose for energy, which we’ll learn more about later.)
Food sources of glucose: Glucose is found in fruits and vegetables, as well as honey, corn syrup, and high fructose corn syrup. (All plants make glucose through photosynthesis as described at the end of this section and in the video.)
2 – Fructose
Fructose is special because it is the sweetest carbohydrate. Plants make fructose as a way of attracting insects and animals, which help plants to reproduce. For example, plants make nectar, which is high in fructose and very sweet, to attract insects that will pollinate it. Plants also put fructose into fruit to make it tastier. Animals eat the fruit, wander away, and later poop out the seeds from the fruit, thereby sowing the seeds of the next generation. Animal gets a meal, and the plant gets to reproduce: win-win!

Food sources of fructose: Fruits, vegetables, honey, high fructose corn syrup
3 – Galactose
Food sources of galactose: Galactose is found in milk (and dairy products made from milk), but it’s almost always linked to glucose to form the disaccharide lactose (more on that in a minute). We rarely find it in our food supply in monosaccharide form.
The second type of simple carbohydrates is disaccharides. They contain two sugar units bonded together.
The Disaccharides: Maltose, Sucrose, and Lactose
The disaccharides consist of two of the monosaccharides described above as shown below.
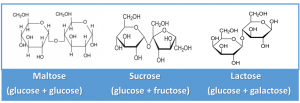
-
Maltose (glucose + glucose)
Maltose is made of two glucose molecules bonded together. It doesn’t occur naturally in appreciable amounts in foods, with one exception: sprouted grains. Grains contain a lot of starch, which is made of long chains of glucose (more on this in a minute), and when the seed of a grain starts to sprout, it begins to break down that starch, creating maltose. If bread is made from those sprouted grains, that bread will have some maltose. Sprouted grain bread is usually a little sweeter than bread made from regular flour.
Maltose also plays a role in the production of beer and liquor, because this process involves the fermentation of grains or other carbohydrate sources. Maltose is formed during the breakdown of those carbohydrates, but there is very little remaining once fermentation is complete.
2 – Sucrose (glucose+ fructose)
Sucrose is made of glucose bonded to fructose . It’s made by plants for the same reason as fructose — to attract animals to eat it and thereby spread the seeds.
Sucrose is naturally-occurring in fruits and vegetables. (Most fruits and vegetables contain a mixture of glucose, fructose, and sucrose.) But humans have also figured out how to concentrate the sucrose in plants (usually sugar cane or sugar beets) to make refined table sugar. We also find sucrose in maple syrup and honey.
The sucrose found in a sweet potato is chemically identical to the sucrose found in table sugar. Likewise, the fructose found in a fig is chemically identical to the fructose found in high fructose corn syrup. As we’ll discuss more later, what’s different is the package the sugars come in. When you eat a sweet potato or a fig, you also get lots of fiber, vitamins, and minerals in that package, whereas sugar and high fructose corn syrup only provide sugar, nothing else. It’s not a bad thing to eat sugar. After all, it’s a vital fuel for our brain and nervous system. But paying attention to the package it comes in can help us make good overall choices for health.
3 – Lactose (glucose+ galactose)
Lactose is made of glucose bonded to galactose. It is sometimes called “milk sugar” and found in dairy products like milk, yogurt, and with a small amount in cheese. These are the only animal foods that have significant amounts of carbohydrate. Most of our carbohydrates come from plant foods.
Complex Carbohydrates: Starch, Glycogen, and Fiber
Complex carbohydrates are also called polysaccharides, because they contain many sugars. (The prefix “poly-” means “many.”) All of the three polysaccharides are made up of many glucose molecules bonded together, but they differ in their structure and the type of bonds.
1 – Starch
Starch is made up of long chains of glucose. If these chains are straight, they’re called amylose; if they’re branched, they’re called amylopectin. Recall that green hexagons represent glucose.
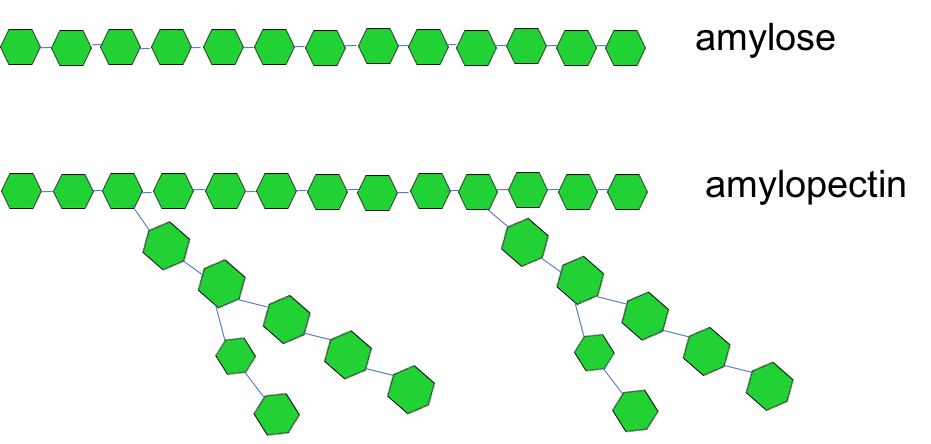
Humans have digestive enzymes to break down both types of starch, which we’ll discuss on the next page.
Starch is the storage form of carbohydrate in plants. It’s made from many glucose molecule attached to each other. Starch in seeds provides the seedling energy to sprout, and we eat those seeds in the form of grains, legumes (soybeans, lentils, pinto and kidney beans), nuts, and seeds. Starch is also stored in roots and tubers to provide stored energy for the plant to grow and reproduce; we eat these in the form of potatoes, sweet potatoes, carrots, beets, and turnips.
When we eat plant foods with starch, we can break it down into glucose to provide fuel for our body’s cells. In addition, starch from whole plant foods comes packaged with other valuable nutrients. We also find refined starch—such as corn starch—as a thickener used in many processed foods.
2 – Glycogen
Glycogen is structurally similar to amylopectin, but it’s the storage form of carbohydrate in animals, humans included. It’s made up of highly branched chains of glucose, and it’s stored in the liver and skeletal muscle. The branched structure of glycogen makes it easier to break down quickly to release glucose to serve as fuel when needed on short notice.
Liver glycogen is broken down to glucose then released into the bloodstream and can be used by cells around the body. Muscle glycogen provides energy only for muscle, to fuel activity. That can come in handy if you’re being chased by a lion, or sprinting to make your bus! Both liver and muscle glycogen serve as relatively short-term forms of energy storage; together, they can only provide enough glucose to last for about 24 hours in a person fasting or eating a very low carbohydrate diet.
Even though glycogen is stored in the liver and muscles of animals, we don’t find it in meat, because it’s broken down soon after slaughter. Thus, glycogen is not found in our food. Instead, we have to make it in our liver and muscle from glucose.
Here’s a beautiful depiction of glycogen.

.
3 – Fiber
Fiber includes carbohydrates and other structural substances in plants that cannot be digestible by human enzymes. Fiber is made by plants to provide protection and structural support. Think about thick stems that help a plant stand upright, tough seed husks, and fruit skin that protect what’s growing inside. These are full of fiber.

In our food, we find fiber in whole plant foods like whole grains, seeds, nuts, fruits, vegetables, and legumes.
One of the most common types of fiber is cellulose, the main component in plant cell walls. The chemical structure of cellulose is shown in the figure below, with our simplified depiction next to it. You can see that cellulose has long chains of glucose, similar to starch, but they’re stacked up, and there are hydrogen bonds linking the stacks.
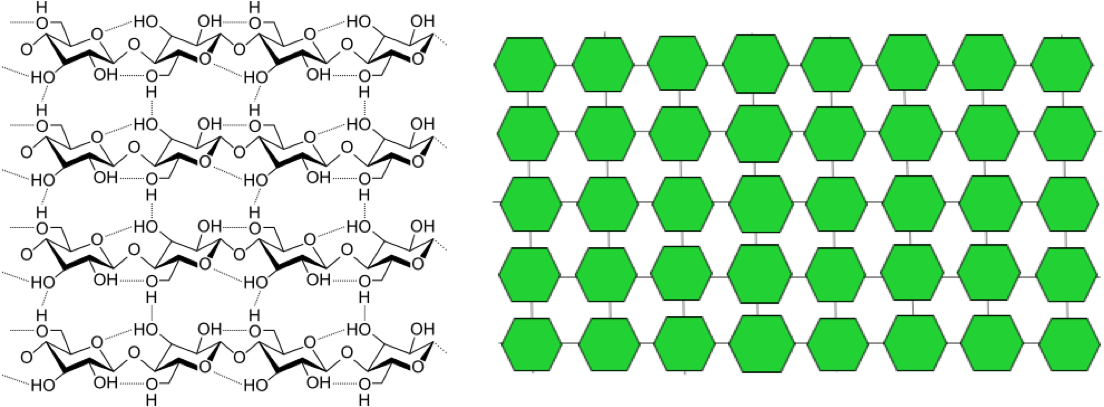
When we eat fiber, it passes through the small intestine intact, because we don’t have digestive enzymes to break it down. Then, in the large intestine, our friendly microbiota—the bacteria that live in our colons—go to work on the fiber. Some fiber can be fermented by those bacteria. We’ll discuss fiber more later in the unit.
Photosynthesis: How Plants Make Glucose
Other than the milk sugar lactose, carbohydrates are derived from plant foods: fruits, vegetables, grains, and legumes. Even sweeteners such as sugar and high fructose corn syrup are made from highly processed plant sources. And each gram of carbs, no matter the source, provides 4 kcal of energy.
So, where do the carbohydrates and the energy they provide come from? A simple process known as photosynthesis.
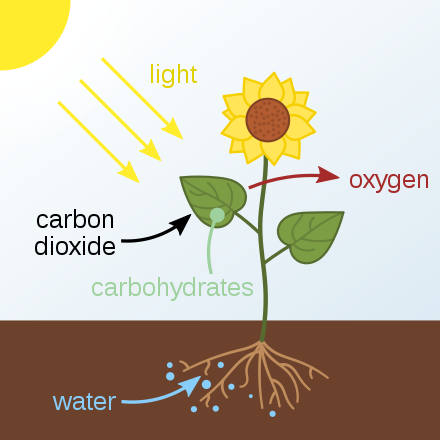
Photosynthesis captures the energy from the sun (the “photo-” part) and stores energy in the carbon-carbon bonds of glucose (the “-synthesis” part). Our bodies can take glucose and break down the carbon-carbon bonds to form the high energy molecule adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
Photosynthesis generally occurs in the leaves of plants in a multi-step process that requires sunlight, carbon dioxide (CO2, found in the air), and water (H2O, from the soil). After the process is complete, the plant releases oxygen into the air (O2, essential for many living organisms) and produces the simple carbohydrate molecule of glucose, which can be used as an energy source by the plant, converted to starch and stored for a later energy source, or converted into other organic molecules such as fats, proteins and vitamins. This glucose is a source of energy that all living organisms need to survive. Plants can covert glucose to fructose, sucrose, maltose, starch and fiber. The only carb not made by plants is the milk sugar lactose.
The 4 minute video “The simple story of photosynthesis and food” describes photosynthesis and gives a preview of how our bodies use carbohydrates. By Amanda Ooten for TED Ed. (Mar 5, 2013)
VIDEO: “The simple story of photosynthesis and food.” TED Ed. By Amanda Ooten (Mar 5, 2013) (4.01 minutes)
Review Questions
References:
- Levin, R. J. (1999). Carbohydrates. In Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease (9th ed.). Baltimore: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture. (n.d.). FoodData Central. Retrieved November 15, 2019, from https://fdc.nal.usda.gov/
Image Credits:
- Figure 4.4. “Types of carbohydrates diagram” by Alice Callahan made with Microsoft SmartArt is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
- “Structure of alpha-D-glucopyranose (Haworth projection)” , “Structure of beta-D-fructofuranose (Haworth projection)” , and “Structure of beta-D-galactopyranose (Haworth projection)” by NEUROtiker is in the Public Domain
- “Simple carbohydrate diagrams” (with hexagons, pentagon) by Alice Callahan is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0
- Maltose structure is cropped from “Amylase reaction consisting of hydrolyzing amylose, producing maltose” by BQmUB2012134 is in the Public Domain, CC0
- “Skeletal formula of sucrose” by NEUROtiker is in the Public Domain, CC0
- ” Lactose (simplified structure)” by NEUROtiker is in the Public Domain, CC0
- Figure 4.5. “Flower with bee” by pontla; “Honey” by sunny mama; “Kiwi” by ereta ekarafi; all licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
- Figure 4.6. “Glycogen” by Häggström, Mikael (2014). “Medical gallery of Mikael Häggström 2014“. WikiJournal of Medicine 1 (2). DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.008. ISSN 2002-4436. Public Domain.
- Figure 4.7. “Wheat” by Bernat Caser; “Broccoli” by albedo20; “Apple” by Fiona Shields; all licensed under CC BY-NC-ND 2.0
- “Chemical structure of cellulose” by laghi.l is licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0

