Should you choose to use a background color, make sure you are consistent throughout your presentation. Different colors portray different meanings, but much of this is cultural and contextual, so there are few hard and fast rules about the meaning of colors. One universal recommendation is to avoid the color red because it has been shown to reduce your ability to think clearly. Bright colors, such as yellow, pink, and orange, should also be avoided as background colors, as they are too distracting. Black, on the other hand, is generally associated with sophistication and can be a very effective background as long as there is sufficient contrast with the other elements on your slide.
When designing your presentation, it is tempting to show off your tech skills with glitzy transitions, wipes, fades, moving text, sounds, and a variety of other actions. These are distracting to your audience and should be avoided. They draw attention away from you and your message, instead focusing the audience’s attention on the screen. Since people naturally look at what is moving and expect it to mean something, meaningless effects, no matter how subtle, distract your audience, and affect their ability to grasp the content. Make sure that all your changes are meaningful and reinforce your message.
Colors
There are complicated and fascinating biological and psychological processes associated with color and color perception that are beyond the scope of this chapter. Because color can have such a huge impact on the ability to see and understand your visuals, this section will explore basic rules and recommendations for working with color.
Much of what we perceive in terms of a color is based on what color is next to it. Be sure to use colors that contrast so they can be easily distinguished from each other (think yellow and dark blue for high contrast, not dark blue and purple). High contrast improves visibility, particularly at a distance. To ensure you have sufficient contrast, you can view your presentation in greyscale either in the software if available or by printing out your slides on a black and white printer.
Color does not add a pleasant quality to design—it reinforces it. – Pierre Bonnard
As seen in Figure 13.7, warm colors (reds, oranges, yellows) appear to come to the foreground when set next to a cool color (blues, grays, purples) which recede into the background. Tints (pure color mixed with white, think pink) stand out against a darker background. Shades (pure color mixed with black, think maroon) recede into a light background. If you want something to stand out, these color combination rules can act as a guide.
Avoid using red and green closely together. Red-green color blindness is the predominate form of color blindness, meaning that the person cannot distinguish between those two colors (Vorick, 2011). There are other forms of color blindness, and you can easily check to see if your visuals will be understandable to everyone using an online tool such as the Coblis Color Blindness Simulator to preview images as a color-blind person would see it. Certain red-blue pairings can be difficult to look at for the non-color blind. These colors appear to vibrate when adjacent to each other and are distracting and sometimes unpleasant to view.
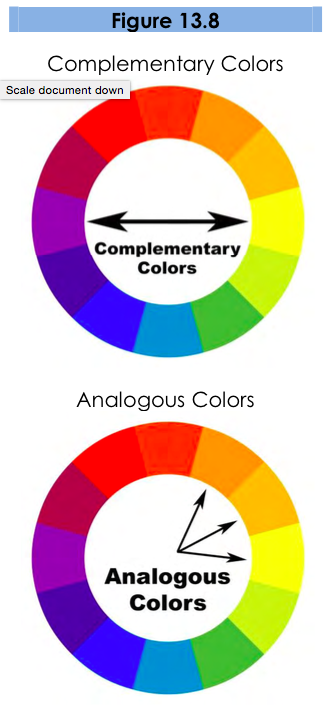
With all these rules in place, selecting a color palette, the group of colors to use throughout your presentation, can be daunting. Some color pairs, like complementary colors or analogous colors as in Figure 13.8, are naturally pleasing to the eye and can be easy options for the color novice. There are also online tools for selecting pleasing color palettes using standard color pairings including Kuler and Color Scheme Designer. You can also use websites like Colorbrewer to help identify an appropriate palette of colors that are visually distinct, appropriate for the colorblind, and that will photocopy well, should you decide to also include this information in a handout.
I’m a visual thinker, not a language-based thinker. My brain is like Google Images. – Temple Grandin
Fonts
There are thousands of fonts available today. One might even say there has been a renaissance in font design with the onset of the digital age. Despite many beautiful options, it is best to stick to standard fonts that are considered screen friendly. These include the serif fonts Times New Roman, Georgia, and Palatino, and the sans serif fonts Ariel, Helvetica, Tahoma, and Veranda. These fonts work well with the limitations of computer screens and are legible from a distance if sized appropriately. Other non-standard fonts, while attractive and eye-catching, may not display properly on all computers. If the font isn’t installed on the computer you are presenting from, the default font will be used which alters the text and design of the slide.
Readability is a top concern with font use, particularly for those at the back of your audience, furthest from the screen. After you have selected a font (see previous paragraph), make sure that the font size is large enough for everyone to read clearly. If you have the opportunity to use the presentation room before the event, view your slides from the back of the room. They should be clearly visible. This is not always possible and should not be done immediately preceding your talk, as you won’t have time to effectively edit your entire presentation. Presentation guru Duarte describes an ingenious way to test visibility from your own computer.
Measure your monitor diagonally in inches, display your slides, then step back the same number of feet as you measured on your monitor in inches. For example, if you have a 17-inch screen, step back 17 feet to see what is legible.
Create your own visual style… let it be unique for yourself and yet identifiable for others. – Orson Welles
In addition to font style and size, there are other font “rules” to improve your slides:
- Don’t use decorative, script, or visually complex fonts.
- Never use the Comic Sans font if you want to retain any credibility with your audience.
- If you must use more than one font, use one serif font and one sans serif font.
- Use the same font(s) and size(s) consistently throughout your presentation.
- Don’t use all upper case or all bold.
- Avoid small caps and all word art, shadows, outlines, stretching text, and other visual effects.
- Use italics and underlines only for their intended purposes, not for design.
While there are many rules listed here, they can be summarized as” keep it as simple as possible.” See Figure 13.9 for examples of poor font choices.
Text
Nothing is more hotly debated in slide design than the amount of text that should be on a slide. Godin says “no more than six words on a slide. EVER.” Other common approaches include the 5×5 rule—5 lines of text, 5 words per line—and similar 6×6 and 7×7 rules. Even with these recommendations, it is still painfully common to see slides with so much text on them that they can’t be read by the audience. The type has to be so small to fit all the words on the slide that no one can read it. Duarte keenly points out that if you have too many words, you no longer have a visual aid. You have either a paper or a teleprompter, and she recommends opting for a small number of words.
Once you understand that the words on the screen are competing for your audience’s attention, it will be easier to edit your slide text down to a minimum. The next time you are watching a presentation and the slide changes, notice how you aren’t really grasping what the speaker is saying, and you also aren’t really understanding what you are reading. Studies have proved this split-attention affects our ability to retain information; so when presenting, you need to give your audience silent reading time when you display a new slide. That is: talk, advance to your next slide, wait for them to read the slide, and resume talking. If you consider how much time your audience is reading rather than listening, hopefully you will decide to reduce the text on your slide and return the focus back to you, the speaker, and your message.
There are several ways to reduce the number of words on your page, but don’t do it haphazardly. As previously discussed, instead of simply abbreviating your message to make it “fit,” consider turning as many concepts as possible into images. Studies have shown that people retain more information when they see images that relate to the words they are hearing. And when people are presented information for a very short time, they remember images better than words.
TIP
An easy way to judge how much time your audience needs to read your slide silently, is to read the slide text to yourself in reverse order.
The ubiquitous use of bulleted lists is also hotly debated. PowerPoint is practically designed around the bulleted-list format, even though is it regularly blamed for dull, tedious presentations with either overly dense or overly superficial content. Mostly this format is used (incorrectly) as a presenter’s outline. “No one can do a good presentation with slide after slide of bullet points. No One.” Reserve bulleted lists for specifications or explaining the order of processes. In all other cases, look for ways to use images, a short phrase, or even no visual at all.
Quotes, on the other hand, are not as offensive to design when they are short, legible, and infrequently used. They can be a very powerful way to hammer a point home or to launch into your next topic. See Figure 13.10 for an example. If you do use a quote in your slide show, immediately stop and read it out loud or allow time for it to be read silently. If the quote is important enough for you to include it in the talk, the quote deserves the audience’s time to read and think about it. Alternately, use a photo of the speaker or of the subject with a phrase from the quote you will be reading them, making the slide enhance the point of the quote.
Images
Images can be powerful and efficient ways to tap into your audience’s emotions. Use photographs to introduce an abstract idea, to evoke emotion, to present evidence, or to direct the audience attention, just make sure it is compatible with your message. Photos aren’t the only images available. You might consider using simplified images like silhouettes, line art, diagrams, enlargements, or exploded views, but these should be high quality and relevant. Simplified can be easier to understand, particularly if you are showing something that has a lot of detail. Simple images also translate better than words to a multicultural audience. In all cases, choose only images that enhance your spoken words and are professional quality. This generally rules out the clip art that comes with slideware, whose use is a sign of amateurism. Select high-quality images and don’t be afraid to use your entire slide to display the image. Boldness with images often adds impact.
When using images, do not enlarge them to the point that the image becomes blurry, also known as pixelation. Pixelation, (Figure 13.11) is caused when the resolution of your image is too low for your output device (e.g. printer, monitor, projector). When selecting images, look for clear ones that can be placed in your presentation without enlarging them. A common practice is to use images over 1,000 pixels wide for filling an entire slide. If your images begin to pixelate, either reduce the size of the image or select a different image.
Never use an image that has a watermark on it, as in Figure 13.2. A watermark is text or a logo that is placed in a digital image to prevent people from re-using it. It is common for companies that sell images to have a preview available that has a watermark on it. This allows you, the potential customer, to see the image, but prevents you from using the image until you have paid for it. Using a watermarked image in your presentation is unprofessional. Select another image without a watermark, take a similar photo yourself, or pay to get the watermark-free version.
You can create images yourself, use free images from places like Pexels, or pay for images from companies like iStockphoto for your presentations. Purchasing images can get expensive quickly and searching for free images is time consuming. Be sure to only use images that you have permission or rights to use and give proper credit for their use. If you are looking for free images, try searching the Creative Commons database for images from places like Flickr, Google, and others. The creators of images with a Creative Commons License allow others to use their work, but with specific restrictions. What is and isn’t allowed is described in the license for each image. Generally, images can be used in educational or non-commercial settings at no cost as long as you give the photographer credit. Also, images created by the U.S. government and its agencies are copyright free and can be used at no cost.
One final consideration with using images: having the same image on every page, be it part of the slide background or your company logo, can be distracting and should be removed or minimized. As mentioned earlier, the more you can simplify your slide, the easier it will be for your audience to understand your message.
Graphs and Charts
As we mentioned in the chapter on support materials, if you have numerical data that you want to present, consider using a graph or chart. You are trying to make a specific point with the data on the slide, so make sure that the point—the conclusion you want your audience to draw—is clear. This may mean that you reduce the amount of data you present, even though it is tempting to include all of your data on your slide.
It is best to minimize the amount of information and focus instead on the simple and clear conclusion. You can include the complete data set in your handout if you feel it is necessary. Particularly when it comes to numerical data, identify the meaning in the numbers and exclude the rest. “Audiences are screaming ‘make it clear,’ not ‘cram more in.’ You won’t often hear an audience member say, ‘That presentation would have been so much better if it were longer.” In some cases you can even ditch the graph altogether and display the one relevant fact that is your conclusion.
|
|
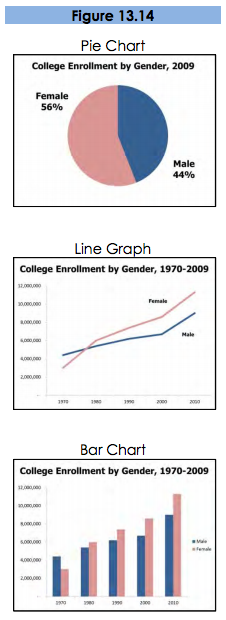 |
Different charts have different purposes, and it is important to select the one that puts your data in the appropriate context to be clearly understood. Pie charts show how the parts relate to the whole and are suitable for up to eight segments, as long as they remain visually distinct. Start your first slice of the pie at 12:00 with your smallest portion and continue around the circle clockwise as the sections increase in size. Usea line graph to show trends over time or how data relates or interacts. Bar charts are good for showing comparisons of size or magnitude and for showing precise comparisons. There are other types of charts and graphs available, but these are the most common.
When designing charts, one should use easily distinguishable colors with clear labels. Be consistent with your colors and data groupings. For clarity, avoid using 3-D graphs and charts, and remove as much of the background noise (lines, shading, etc.) as possible. All components of your graph, once the clutter is removed, should be distinct from any background color. Finally, don’t get too complex in any one graph, make sure your message is as clear as possible, and make sure to visually highlight the conclusion you want the audience to draw.