Chapter 5: Theories of Motivation
Theories of Motivation
What inspires employees to provide excellent service, market a company’s products effectively, or achieve the goals set for them? Answering this question is of utmost importance if we are to understand and manage the work behavior of our peers, subordinates, and even supervisors. Put a different way, if someone is not performing well, what could be the reason?
Job performance is viewed as a function of three factors and is expressed with the equation below (Mitchell, 1982; Porter & Lawler, 1968). According to this equation, motivation, ability, and environment are the major influences over employee performance.

Performance is a function of the interaction between an individual’s motivation, ability, and environment.
Motivation is one of the forces that lead to performance. Motivation is defined as the desire to achieve a goal or a certain performance level, leading to goal-directed behavior. When we refer to someone as being motivated, we mean that the person is trying hard to accomplish a certain task. Motivation is clearly important if someone is to perform well; however, it is not sufficient. Ability—or having the skills and knowledge required to perform the job—is also important and is sometimes the key determinant of effectiveness. Finally, environmental factors such as having the resources, information, and support one needs to perform well are critical to determine performance. At different times, one of these three factors may be the key to high performance. For example, for an employee sweeping the floor, motivation may be the most important factor that determines performance. In contrast, even the most motivated individual would not be able to successfully design a house without the necessary talent involved in building quality homes. Being motivated is not the same as being a high performer and is not the sole reason why people perform well, but it is nevertheless a key influence over our performance level.
So what motivates people? Why do some employees try to reach their targets and pursue excellence while others merely show up at work and count the hours? As with many questions involving human beings, the answer is anything but simple. Instead, there are several theories explaining the concept of motivation. We will discuss motivation theories under two categories: need-based theories and process theories.
7.1 A Motivating Place to Work: The Case of Zappos
Warning: This example is an excellent resource but it should be noted that Tony Hseicich tragically passed away in 2020. Reviewing his concepts of motivation are relevant, however if you opt not to review, it will not have an impact on your overall grade in the course. It is unique to hear about a CEO who studies happiness and motivation and builds those principles into the company’s core values or about a company with a 5-week training course and an offer of $2,000 to quit any- time during that 5 weeks if you feel the company is not a good fit. Top that off with an on-site life coach who also happens to be a chiropractor, and you are really talking about something you don’t hear about every day. Zappos is known as much for its 365-day return policy and free shipping as it is for its innovative corporate culture. Although acquired in 2009 by Amazon (NASDAQ: AMZN), Zappos managed to move from number 23 in 2009 on Fortune magazine’s “100 Best Companies to Work For” list to 15 in 2010.
Performance is a function of motivation, ability, and the environment in which you work. Zappos seems to be creating an environment that encourages motivation and builds inclusiveness. The company delivers above and beyond basic workplace needs and addresses the self-actualization needs that most individuals desire from their work experience. CEO Tony Hsieh believes that the secret to customer loyalty is to make a corporate culture of caring a priority. This is reflected in the company’s 10 core values and its emphasis on building a team and a family. During the interview process, applicants are asked questions relating to the company’s values, such as gauging their own weirdness, open-mindedness, and sense of family. Although the offer to be paid to quit during the training process has increased from its original number of $400, only 1% of trainees take the offer. Work is structured differently at Zappos as well. For example, there is no limit to the time customer service representatives spend on a phone call, and they are encouraged to make personal connections with the individuals on the other end rather than try to get rid of them.
Although Zappos has over 1,300 employees, the company has been able to maintain a relatively flat organizational structure and prides itself on its extreme transparency. In an exceptionally detailed and lengthy letter to employees, Hsieh spelled out what the new partnership with Amazon would mean for the company, what would change, and more important, what would remain the same. As a result of this type of company structure, individuals have more freedom, which can lead to greater satisfaction.
Although Zappos pays its employees well and offers attractive benefits such as employees receiving full health-care coverage and a compressed workweek, the desire to work at Zappos seems to go beyond that. As Hsieh would say, happiness is the driving force behind almost any action an individual takes. Whether your goals are for achievement, affiliation, or simply to find an enjoyable environment in which to work, Zappos strives to address these needs.
Based on information from Robischon, N. (2009, July 22). Amazon buys Zappos for $847 million. Fast Company. Retrieved February 28, 2010, from http://www.fastcompany.com/blog/noah-robischon/editors-desk/ amazon-buys-zappos-807-million; Walker, A. (2009, March 14). Zappos’ Tony Hsieh on Twitter, phone calls and the pursuit of happiness. Fast Company. Retrieved February 27, 2010, from http://www.fastcom- pany.com/blog/alissa-walker/member-blog/tony-hsiehs-zapposcom; Happy feet—Inside the online shoe utopia. (2009, September 14). New Yorker. Retrieved February 28, 2010, from http://about.zappos.com/press- center/media-coverage/happy-feet-inside-online-shoe-utopia; 100 best companies to work for. (2010, February 8). Fortune. Retrieved February 26, 2010, from http://money.cnn.com/magazines/fortune/bestcompanies/ 2010/snapshots/15.html.
7.2 Need-Based Theories of Motivation
The earliest studies of motivation involved an examination of individual needs. Specifically, early researchers thought that employees try hard and demonstrate goal-driven behavior in order to satisfy needs. For example, an employee who is always walking around the office talking to people may have a need for companionship, and his behavior may be a way of satisfying this need. At the time, researchers developed theories to understand what people need. Four theories may be placed under this category: Maslow’s hierarchy of needs, ERG theory, Herzberg’s two-factor theory, and McClelland’s acquired- needs theory.
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Abraham Maslow is among the most prominent psychologists of the twentieth century. His hierarchy of needs is an image familiar to most business students and managers. The theory is based on a simple premise: Human beings have needs that are hierarchically ranked (Maslow, 1943; Maslow, 1954). There are some needs that are basic to all human beings, and in their absence nothing else matters. As we satisfy these basic needs, we start looking to satisfy higher order needs. In other words, once a lower level need is satisfied, it no longer serves as a motivator.
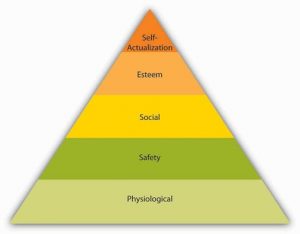
The most basic of Maslow’s needs are physiological needs. Physiological needs refer to the need for food, water, and other biological needs. These needs are basic because when they are lacking, the search for them may overpower all other urges. Imagine being very hungry. At that point, all your behavior may be directed at finding food. Once you eat, though, the search for food ceases and the promise of food no longer serves as a motivator. Once physiological needs are satisfied, people tend to become concerned about safety needs. Are they free from the threat of danger, pain, or an uncertain future? On the next level up, social needs refer to the need to bond with other human beings, be loved, and form lasting attachments with others. In fact, attachments, or lack of them, are associated with our health and well-being (Baumeister & Leary, 1995). The satisfaction of social needs makes esteem needs more salient. Esteem need refers to the desire to be respected by one’s peers, feel important, and be appreciated. Finally, at the highest level of the hierarchy, the need for self-actualization refers to “becoming all you are capable of becoming.” This need manifests itself by the desire to acquire new skills, take on new challenges, and behave in a way that will lead to the attainment of one’s life goals.
Maslow was a clinical psychologist, and his theory was not originally designed for work settings. In fact, his theory was based on his observations of individuals in clinical settings; some of the individual components of the theory found little empirical support. One criticism relates to the order in which the needs are ranked. It is possible to imagine that individuals who go hungry and are in fear of their lives might retain strong bonds to others, suggesting a different order of needs. Moreover, researchers failed to support the arguments that once a need is satisfied it no longer serves as a motivator and that only one need is dominant at a given time (Neher, 1991; Rauschenberger, Schmitt, & Hunter, 1980).
Despite the lack of strong research support, Maslow’s theory found obvious applications in business settings. Understanding what people need gives us clues to understanding them. The hierarchy is a systematic way of thinking about the different needs employees may have at any given point and explains different reactions they may have to similar treatment. An employee who is trying to satisfy esteem needs may feel gratified when her supervisor praises an accomplishment. However, another employee who is trying to satisfy social needs may resent being praised by upper management in front of peers if the praise sets the individual apart from the rest of the group.
How can an organization satisfy its employees’ various needs? In the long run, physiological needs may be satisfied by the person’s paycheck, but it is important to remember that pay may satisfy other needs such as safety and esteem as well. Providing generous benefits that include health insurance and company-sponsored retirement plans, as well as offering a measure of job security, will help satisfy safety needs. Social needs may be satisfied by having a friendly environment and providing a workplace conducive to collaboration and communication with others. Company picnics and other social get-togethers may also be helpful if the majority of employees are motivated primarily by social needs (but may cause resentment if they are not and if they have to sacrifice a Sunday afternoon for a company picnic). Pro- viding promotion opportunities at work, recognizing a person’s accomplishments verbally or through more formal reward systems, and conferring job titles that communicate to the employee that one has achieved high status within the organization are among the ways of satisfying esteem needs. Finally, self-actualization needs may be satisfied by the provision of development and growth opportunities on or off the job, as well as by work that is interesting and challenging. By making the effort to satisfy the different needs of each employee, organizations may ensure a highly motivated workforce.
ERG Theory
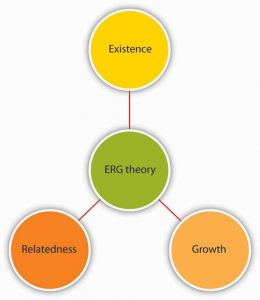
Source: Based on Alderfer, C. P. (1969). An empirical test of a new theory of human needs. Organizational Behavior and Human Performance, 4, 142–175.
ERG theory, developed by Clayton Alderfer, is a modification of Maslow’s hierarchy of needs (Alderfer, 1969). Instead of the five needs that are hierarchically organized, Alderfer proposed that basic human needs may be grouped under three categories, namely, existence, relatedness, and growth. Existence corresponds to Maslow’s physiological and safety needs, relatedness corresponds to social needs, and growth refers to Maslow’s esteem and self-actualization. ERG theory’s main contribution to the literature is its relaxation of Maslow’s assumptions. For example, ERG theory does not rank needs in any particular order and explicitly recognizes that more than one need may operate at a given time. Moreover, the theory has a “frustration-regression” hypothesis suggesting that individuals who are frustrated in their attempts to satisfy one need may regress to another. For example, someone who is frustrated by the growth opportunities in his job and progress toward career goals may regress to relatedness need and start spending more time socializing with coworkers. The implication of this theory is that we need to recognize the multiple needs that may be driving individuals at a given point to understand their behavior and properly motivate them.
Two-Factor Theory
Frederick Herzberg approached the question of motivation in a different way. By asking individuals what satisfies them on the job and what dissatisfies them, Herzberg came to the conclusion that aspects of the work environment that satisfy employees are very different from aspects that dissatisfy them (Herzberg, Mausner, & Snyderman, 1959; Herzberg, 1965). Herzberg labeled factors causing dissatisfaction of workers as “hygiene” factors because these factors were part of the context in which the job was performed, as opposed to the job itself. Hygiene factors included company policies, supervision, working conditions, salary, safety, and security on the job. To illustrate, imagine that you are working in an unpleasant work environment. Your office is too hot in the summer and too cold in the winter. You are being harassed and mistreated. You would certainly be miserable in such a work environment. How- ever, if these problems were solved (your office temperature is just right and you are not harassed at all), would you be motivated? Most likely, you would take the situation for granted. In fact, many factors in our work environment are things that we miss when they are absent but take for granted if they are present.
In contrast, motivators are factors that are intrinsic to the job, such as achievement, recognition, interesting work, increased responsibilities, advancement, and growth opportunities. According to Herzberg’s research, motivators are the conditions that truly encourage employees to try harder.
Hygiene Factors |
Motivators |
| Company Policy | Achievement |
| Supervision and relationships | Recognition |
| Working Conditions | Interesting work |
| Salary | Increased responsibility |
| Security | Advancement an growth |
The two-factor theory of motivation includes hygiene factors and motivators.
Sources: Based on Herzberg, F., Mausner, B., & Snyderman, B. (1959). The motivation to work. New York: John Wiley and Sons; Herzberg, F. (1965). The motivation to work among Finnish supervisors. Personnel Psychology, 18, 393–402.
Herzberg’s research is far from being universally accepted (Cummings & Elsalmi, 1968; House & Wigdor, 1967). One criticism relates to the primary research methodology employed when arriving at hygiene versus motivators. When people are asked why they are satisfied, they may attribute the causes of satisfaction to themselves, whereas when explaining what dissatisfies them, they may blame the situation. The classification of the factors as hygiene or motivator is not that simple either. For example, the theory views pay as a hygiene factor. However, pay may have symbolic value by showing employees that they are being recognized for their contributions as well as communicating that they are advancing within the company. Similarly, the quality of supervision or the types of relationships employees form with their supervisors may determine whether they are assigned interesting work, whether they are recognized for their potential, and whether they take on more responsibilities.
Despite its limitations, the theory can be a valuable aid to managers because it points out that improving the environment in which the job is performed goes only so far in motivating employees. Undoubtedly, contextual factors matter because their absence causes dissatisfaction. However, solely focusing on hygiene factors will not be enough, and managers should also enrich jobs by giving employees opportunities for challenging work, greater responsibilities, advancement opportunities, and a job in which their subordinates can feel successful.
Acquired-Needs Theory
Among the need-based approaches to motivation, David McClelland’s acquired-needs theory is the one that has received the greatest amount of support. According to this theory, individuals acquire three types of needs as a result of their life experiences. These needs are the need for achievement, the need for affiliation, and the need for power. All individuals possess a combination of these needs, and the dominant needs are thought to drive employee behavior.
McClelland used a unique method called the Thematic Apperception Test (TAT) to assess the dominant need (Spangler, 1992). This method entails presenting research subjects an ambiguous picture asking them to write a story based on it. Take a look at the following picture. Who is this person? What is she doing? Why is she doing it? The story you tell about the woman in the picture would then be analyzed by trained experts. The idea is that the stories the photo evokes would reflect how the mind works and what motivates the person.
If the story you come up with contains themes of success, meeting deadlines, or coming up with brilliant ideas, you may be high in need for achievement. Those who have high need for achievement have a strong need to be successful. As children, they may be praised for their hard work, which forms the foundations of their persistence (Mueller & Dweck, 1998). As adults, they are preoccupied with doing things better than they did in the past. These individuals are constantly striving to improve their performance. They relentlessly focus on goals, particularly stretch goals that are challenging in nature (Campbell, 1982). They are particularly suited to positions such as sales, where there are explicit goals, feedback is immediately available, and their effort often leads to success. In fact, they are more attracted to organizations that are merit-based and reward performance rather than seniority. They also do particularly well as entrepreneurs, scientists, and engineers (Harrell & Stahl, 1981; Trevis & Certo, 2005; Turban & Keon, 1993).
Are individuals who are high in need for achievement effective managers? Because of their success in lower level jobs where their individual contributions matter the most, those with high need for achievement are often promoted to higher level positions (McClelland & Boyatzis, 1982). However, a high need for achievement has significant disadvantages in management positions. Management involves getting work done by motivating others. When a salesperson is promoted to be a sales manager, the job description changes from actively selling to recruiting, motivating, and training salespeople. Those who are high in need for achievement may view managerial activities such as coaching, communicating, and meeting with subordinates as a waste of time and may neglect these aspects of their jobs. Moreover, those high in need for achievement enjoy doing things themselves and may find it difficult to delegate any meaningful authority to their subordinates. These individuals often micromanage, expecting others to approach tasks a particular way, and may become overbearing bosses by expecting everyone to display high levels of dedication (McClelland & Burnham, 1976).
If the story you created in relation to the picture you are analyzing contains elements of making plans to be with friends or family, you may have a high need for affiliation. Individuals who have a high need for affiliation want to be liked and accepted by others. When given a choice, they prefer to interact with others and be with friends (Wong & Csikszentmihalyi, 1991). Their emphasis on harmonious interpersonal relationships may be an advantage in jobs and occupations requiring frequent interpersonal interaction, such as a social worker or teacher. In managerial positions, a high need for affiliation may again serve as a disadvantage because these individuals tend to be overly concerned about how they are perceived by others. They may find it difficult to perform some aspects of a manager’s job such as giving employees critical feedback or disciplining poor performers. Thus, the work environment may be characterized by mediocrity and may even lead to high performers leaving the team.
Finally, if your story contains elements of getting work done by influencing other people or desiring to make an impact on the organization, you may have a high need for power. Those with a high need for power want to influence others and control their environment. A need for power may in fact be a destructive element in relationships with colleagues if it takes the form of seeking and using power for one’s own good and prestige. However, when it manifests itself in more altruistic forms such as changing the way things are done so that the work environment is more positive, or negotiating more resources for one’s department, it tends to lead to positive outcomes. In fact, the need for power is viewed as an important trait for effectiveness in managerial and leadership positions (McClelland & Burnham, 1976; Spangler & House, 1991; Spreier, 2006).
McClelland’s theory of acquired needs has important implications for the motivation of employees. Managers need to understand the dominant needs of their employees to be able to motivate them. While people who have a high need for achievement may respond to goals, those with a high need for power may attempt to gain influence over those they work with, and individuals high in their need for affiliation may be motivated to gain the approval of their peers and supervisors. Finally, those who have a high drive for success may experience difficulties in managerial positions, and making them aware of common pitfalls may increase their effectiveness.
Key Takeaways
Need-based theories describe motivated behavior as individuals’ efforts to meet their needs. According to this perspective, the manager’s job is to identify what people need and make the work environment a means of satisfying these needs. Maslow’s hierarchy describes five categories of basic human needs, including physio- logical, safety, social, esteem, and self-actualization needs. These needs are hierarchically ranked, and as a lower level need is satisfied, it no longer serves as a motivator. ERG theory is a modification of Maslow’s hierarchy, in which the five needs are collapsed into three categories (existence, relatedness, and growth). The theory recognizes that when employees are frustrated while attempting to satisfy higher level needs, they may regress. The two-factor theory differentiates between factors that make people dissatisfied on the job (hygiene factors) and factors that truly motivate employees (motivators). Finally, acquired-needs theory argues that individuals possess stable and dominant motives to achieve, acquire power, or affiliate with others. The type of need that is dominant will drive behavior. Each of these theories explains characteristics of a work environment that motivates employees. These theories paved the way to process-based theories that explain the mental calculations employees make to decide how to behave.
7.3 Process-Based Theories
A separate stream of research views motivation as something more than action aimed at satisfying a need. Instead, process-based theories view motivation as a rational process. Individuals analyze their environment, develop thoughts and feelings, and react in certain ways. Process theories attempt to explain the thought processes of individuals who demonstrate motivated behavior. Under this category, we will review equity theory, expectancy theory, and reinforcement theory.
Equity Theory
Imagine that you are paid $10 an hour working as an office assistant. You have held this job for 6 months. You are very good at what you do, you come up with creative ways to make things easier around you, and you are a good colleague who is willing to help others. You stay late when necessary and are flexible if requested to change hours. Now imagine that you found out they are hiring another employee who is going to work with you, who will hold the same job title, and who will perform the same type of tasks. This particular person has more advanced computer skills, but it is unclear whether these will be used on the job. The starting pay for this person will be $14 an hour. How would you feel? Would you be as motivated as before, going above and beyond your duties? How would you describe what you would be feeling?

Source: Based on Adams, J. S. (1965). Inequity in social exchange. In L. Berkowitz (Ed.), Advances in experimental social psychology: Vol. 2 (pp. 267–299). New York: Academic Press.
If your reaction to this scenario is along the lines of “this would be unfair,” your behavior may be explained using equity theory (Adams, 1965). According to this theory, individuals are motivated by a sense of fairness in their interactions. Moreover, our sense of fairness is a result of the social comparisons we make. Specifically, we compare our inputs and outcomes with other people’s inputs and outcomes. We perceive fairness if we believe that the input-to-outcome ratio we are bringing into the situation is similar to the input-to-outcome ratio of a comparison person, or a referent. Perceptions of inequity create tension within us and drive us to action that will reduce perceived inequity.
What Are Inputs and Outcomes?
Inputs are the contributions people feel they are making to the environment. In the previous example, the person’s hard work; loyalty to the organization; amount of time with the organization; and level of education, training, and skills may have been relevant inputs. Outcomes are the perceived rewards someone can receive from the situation. For the hourly wage employee in our example, the $10 an hour pay rate was a core outcome. There may also be other, more peripheral outcomes, such as acknowledgment or preferential treatment from a manager. In the prior example, however, the person may reason as follows: I have been working here for 6 months. I am loyal, and I perform well (inputs). I am paid $10 an hour for this (outcomes). The new person does not have any experience here (referent’s inputs) but will be paid $14 an hour. This situation is unfair.
We should emphasize that equity perceptions develop as a result of a subjective process. Different people may look at the same situation and perceive different levels of equity. For example, another person may look at the same scenario and decide that the situation is fair because the newcomer has computer skills and the company is paying extra for those skills.
Who Is the Referent?
The referent other may be a specific person as well as a category of people. Referents should be comparable to us—otherwise the comparison is not meaningful. It would be pointless for a student worker to compare himself to the CEO of the company, given the differences in the nature of inputs and outcomes. Instead, individuals may compare themselves to someone performing similar tasks within the same organization or, in the case of a CEO, a different organization.
Reactions to Unfairness
The theory outlines several potential reactions to perceived inequity. Oftentimes, the situation may be dealt with perceptually by altering our perceptions of our own or the referent’s inputs and outcomes. For example, we may justify the situation by downplaying our own inputs (I don’t really work very hard on this job), valuing our outcomes more highly (I am gaining valuable work experience, so the situation is not that bad), distorting the other person’s inputs (the new hire really is more competent than I am and deserves to be paid more), or distorting the other person’s outcomes (she gets $14 an hour but will have to work with a lousy manager, so the situation is not unfair). Another option would be to have the referent increase inputs. If the other person brings more to the situation, getting more out of the situation would be fair. If that person can be made to work harder or work on more complicated tasks, equity would be achieved. The person experiencing a perceived inequity may also reduce inputs or attempt to increase outcomes. If the lower paid person puts forth less effort, the perceived inequity would be reduced. Research shows that people who perceive inequity reduce their work performance or reduce the quality of their inputs (Carrell & Dittrich, 1978; Goodman & Friedman, 1971). Increasing one’s outcomes can be achieved through legitimate means such as negotiating a pay raise. At the same time, research shows that those feeling inequity sometimes resort to stealing to balance the scales (Green- berg, 1993). Other options include changing the comparison person (e.g., others doing similar work in different organizations are paid only minimum wage) and leaving the situation by quitting (Schmidt & Marwell, 1972). Sometimes it may be necessary to consider taking legal action as a potential outcome of perceived inequity. For example, if an employee finds out the main reason behind a pay gap is gender related, the person may react to the situation by taking legal action because sex discrimination in pay is illegal in the United States.
Potential Responses to Inequity
Reactions to inequity |
Example |
| Distort perceptions | Changing one’s thinking to believe that the referent actually is more skilled than previously thought |
| Increase referent’s inputs | Encouraging the referent to work harder |
| Reduce own input | Deliberately putting forth less effort at work. Reducing the quality of one’s work |
| Increase own outcomes | Negotiating a raise for oneself or using unethical ways of increasing rewards such as stealing from the company |
| Change referent | Comparing oneself to someone who is worse off |
| Leave the situation | Quitting one’s job |
| Seek legal action | Suing the company or filing a complaint if the unfairness in question is under legal protection |
Source: Based on research findings reported in Carrell, M. R., & Dittrich, J. E. (1978). Equity theory: The recent literature, methodological considerations, and new directions. Academy of Management Review, 3, 202–210; Goodman, P. S., & Friedman, A. (1971). An examination of Adams’s theory of inequity. Administrative Science Quarterly, 16, 271–288; Greenberg, J. (1993). Stealing in the name of justice: Informational and interpersonal moderators of theft reactions to underpayment inequity. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 54, 81–103; Schmidt, D. R., & Marwell, G. (1972). Withdrawal and reward reallocation as responses to inequity. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 8, 207–211.
Overpayment Inequity
What would you do if you felt you were over-rewarded? In other words, how would you feel if you were the new employee in our student-worker scenario? Originally, equity theory proposed that over- rewarded individuals would experience guilt and would increase their effort to restore perceptions of equity. However, research does not provide support for this argument. Instead, it seems that individuals experience less distress as a result of being over-rewarded (Austin & Walster, 1974). It is not hard to imagine that individuals find perceptual ways to deal with a situation like this, such as believing they have more skills and bring more to the situation compared to the referent person. Therefore, research does not support equity theory’s predictions with respect to people who are overpaid (Evan & Simmons, 1969).
Individual Differences in Reactions to Inequity
So far, we have assumed that once people feel a situation is inequitable, they will be motivated to react. However, does inequity disturb everyone equally? Researchers have identified a personality trait that explains different reactions to inequity and named this trait as equity sensitivity (Huseman, Hatfield, & Miles, 1987). Equity-sensitive individuals expect to maintain equitable relationships, and they experience distress when they feel they are over-rewarded or under-rewarded. At the same time, there are some individuals who are benevolents, those who give without waiting to receive much in return, and entitleds, who expect to receive substantial compensation for relatively little input. Therefore, the theory is more useful in explaining the behavior of equity-sensitive individuals, and organizations will need to pay particular attention to how these individuals view their relationships.
Fairness Beyond Equity: Procedural and Interactional Justice
Equity theory looks at perceived fairness as a motivator. However, the way equity theory defines fairness is limited to fairness of rewards. Starting in the 1970s, research on workplace fairness began taking a broader view of justice. Equity theory deals with outcome fairness, and therefore it is considered to be a distributive justice theory. Distributive justice refers to the degree to which the outcomes received from the organization are perceived to be fair. Two other types of fairness have been identified: procedural justice and interactional justice.
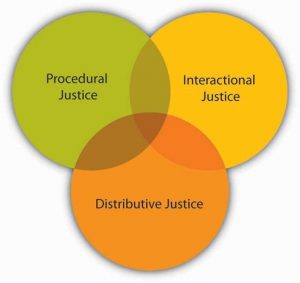
Let’s assume that you just found out you are getting a promotion. Clearly, this is an exciting outcome and comes with a pay raise, increased responsibilities, and prestige. If you feel you deserve to be promoted, you would perceive high distributive justice (your getting the promotion is fair). However, you later found out upper management picked your name out of a hat! What would you feel? You might still like the outcome but feel that the decision-making process was unfair. If so, you are describing feelings of procedural justice. Procedural justice refers to the degree to which fair decision-making procedures are used to arrive at a decision. People do not care only about reward fairness. They also expect decision- making processes to be fair. In fact, research shows that employees care about the procedural justice of many organizational decisions, including layoffs, employee selection, surveillance of employees, performance appraisals, and pay decisions (Alge, 2001; Bauer et al., 1998; Kidwell, 1995). People also tend to care more about procedural justice in situations in which they do not get the outcome they feel they deserve (Brockner & Wisenfeld, 1996). If you did not get the promotion and later discovered that management chose the candidate by picking names out of a hat, how would you feel? This may be viewed as adding insult to injury. When people do not get the rewards they want, they tend to hold management responsible if procedures are not fair (Brockner et al., 2007).
Why do employees care about procedural justice? There are three potential reasons (Cropanzano, Bowen, & Gilliland, 2007; Tyler, 1994; Tyler, Degoey, & Smith, 1996). First, people tend to believe that fairness is an end in itself and it is the right thing to do. Second, fair processes guarantee future rewards. If your name was picked out of a hat, you have no control over the process, and there is no guarantee that you will get future promotions. If the procedures are fair, you are more likely to believe that things will work out in the future. Third, fairness communicates that the organization values its employees and cares about their well-being.
Research has identified many ways of achieving procedural justice. For example, giving employees advance notice before laying them off, firing them, or disciplining them is perceived as fair (Kidwell, 1995). Advance notice helps employees get ready for the changes facing them or gives them an opportunity to change their behavior before it is too late. Allowing employees voice in decision making is also important (Alge, 2001; Kernan & Hanges, 2002; Lind, Kanfer, & Earley, 1990). When designing a performance-appraisal system or implementing a reorganization, it may be a good idea to ask people for their input because it increases perceptions of fairness. Even when it is not possible to have employees participate, providing explanations to employees is helpful in fostering procedural justice (Schaubroeck, May, & William, 1994). Finally, people expect consistency in treatment (Bauer et al., 1998). If one per- son is given extra time when taking a test while another is not, individuals would perceive decision making as unfair.
Now let’s imagine the moment your boss told you that you are getting a promotion. Your manager’s exact words were, “Yes, we are giving you the promotion. The job is so simple that we thought even you can handle it.” Now what is your reaction? The feeling of unfairness you may now feel is explained by interactional justice. Interactional justice refers to the degree to which people are treated with respect, kindness, and dignity in interpersonal interactions. We expect to be treated with dignity by our peers, supervisors, and customers. When the opposite happens, we feel angry. Even when faced with negative outcomes such as a pay cut, being treated with dignity and respect serves as a buffer and alleviates our stress (Greenberg, 2006).
Toolbox: Be a Fair Person!
- When distributing rewards, make sure you pay attention to different contribution levels of employees. Treating everyone equally could be unfair if they participated and contributed at different levels. People who are more qualified, skilled, or those who did more than others expect to receive a greater share of rewards.
- Sometimes you may have to disregard people’s contributions to distribute certain rewards. Some rewards or privileges may be better distributed equally (e.g., health insurance) or based on the particular employee’s needs (such as unpaid leave for health reasons).
- Pay attention to how you make decisions. Before making a decision, ask people to give you their opinions if possible. Explain your decisions to people who are affected by it. Before implementing a change, give people advance notice. Enforce rules consistently among employees.
- Pay attention to how you talk to people. Treat others the way you want to be treated. Be kind, courteous, and considerate of their feelings.
- Remember that justice is in the eye of the beholder. Even when you feel you are being fair, others may not feel the same way, and it is their perception that counts. Therefore, pay attention to being perceived as fair.
- People do not care only about their own justice level. They also pay attention to how others are treated as well. Therefore, in addition to paying attention to how specific employees feel, creating a sense of justice in the entire organization is important.
Sources: Adapted from ideas in Colquitt, J. A. (2004). Does the justice of the one interact with the justice of the many? Reactions to procedural justice in teams. Journal of Applied Psychology, 89, 633–646; Cropanzano, R., Bowen, D. E., & Gilliland, S. W. (2007). The management of organizational justice. Academy of Management Perspectives, 21, 34–48.
Employers would benefit from paying attention to all three types of justice perceptions. In addition to being the right thing to do, paying attention to justice perceptions leads to outcomes companies care about. Injustice is directly harmful to employees’ psychological health and well-being and contributes to stress (Greenberg, 2004; Tepper, 2001). High levels of justice create higher levels of employee commitment to organizations, and they are related to higher job performance, higher levels of organizational citizenship (behaviors that are not part of one’s job description but help the organization in other ways, such as speaking positively about the company and helping others), and higher levels of customer satisfaction. Conversely, low levels of justice lead to retaliation and support of unionization (Blader, 2007; Cohen-Charash & Spector, 2001; Colquitt et al., 2001; Cropanzano, Bowen, & Gilliland, 2007; Master- son, 2001; Masterson et al., 2000; Moorman, 1991; Skarlicki & Folger, 1997).
Expectancy Theory
According to expectancy theory, individual motivation to put forth more or less effort is determined by a rational calculation in which individuals evaluate their situation (Porter & Lawler, 1968; Vroom, 1964). According to this theory, individuals ask themselves three questions.
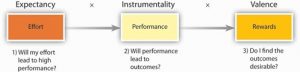
Sources: Based on Porter, L. W., & Lawler, E. E. (1968). Managerial attitudes and performance. Homewood, IL: Irwin; Vroom, V. H. (1964). Work and motivation. New York: Wiley.
The first question is whether the person believes that high levels of effort will lead to outcomes of interest, such as performance or success. This perception is labeled expectancy. For example, do you believe that the effort you put forth in a class is related to performing well in that class? If you do, you are more likely to put forth effort.
The second question is the degree to which the person believes that performance is related to subsequent outcomes, such as rewards. This perception is labeled instrumentality. For example, do you believe that getting a good grade in the class is related to rewards such as getting a better job, or gaining approval from your instructor, or from your friends or parents? If you do, you are more likely to put forth effort.
Finally, individuals are also concerned about the value of the rewards awaiting them as a result of performance. The anticipated satisfaction that will result from an outcome is labeled valence. For example, do you value getting a better job, or gaining approval from your instructor, friends, or parents? If these outcomes are desirable to you, your expectancy and instrumentality is high, and you are more likely to put forth effort.
Expectancy theory is a well-accepted theory that has received a lot of research attention (Heneman & Schwab, 1972; Van Eerde & Thierry, 1996). It is simple and intuitive. Consider the following example. Let’s assume that you are working in the concession stand of a movie theater. You have been selling an average of 100 combos of popcorn and soft drinks a day. Now your manager asks you to increase this number to 300 combos a day. Would you be motivated to try to increase your numbers? Here is what you may be thinking:
- Expectancy: Can I do it? If I try harder, can I really achieve this number? Is there a link between how hard I try and whether I reach this goal or not? If you feel that you can achieve this number if you try, you have high expectancy.
- Instrumentality: What is in it for me? What is going to happen if I reach 300? What are the outcomes that will follow? Are they going to give me a 2% pay raise? Am I going to be named the salesperson of the month? Am I going to receive verbal praise from my manager? If you believe that performing well is related to certain outcomes, instrumentality is high.
- Valence: How do I feel about the outcomes in question? Do I feel that a 2% pay raise is desirable? Do I find being named the salesperson of the month attractive? Do I think that being praised by my manager is desirable? If your answers are yes, valence is positive. In contrast, if you find the outcomes undesirable (you definitely do not want to be named the salesperson of the month because your friends would make fun of you), valence is negative.
If your answers to all three questions are affirmative—you feel that you can do it, you will get an out- come if you do it, and you value the reward—you are more likely to be motivated to put forth more effort toward selling more combos.
As a manager, how can you motivate employees? In fact, managers can influence all three perceptions (Cook, 1980).
Influencing Expectancy Perceptions
Employees may not believe that their effort leads to high performance for a multitude of reasons. First, they may not have the skills, knowledge, or abilities to successfully perform their jobs. The answer to this problem may be training employees or hiring people who are qualified for the jobs in question. Second, low levels of expectancy may be because employees may feel that something other than effort predicts performance, such as political behaviors on the part of employees. If employees believe that the work environment is not conducive to performing well (resources are lacking or roles are unclear), expectancy will also suffer. Therefore, clearing the path to performance and creating an environment in which employees do not feel restricted will be helpful. Finally, some employees may perceive little connection between their effort and performance level because they have an external locus of control, low self-esteem, or other personality traits that condition them to believe that their effort will not make a difference. In such cases, providing positive feedback and encouragement may help motivate employees.
Influencing Instrumentality Perceptions
Showing employees that their performance is rewarded is going to increase instrumentality perceptions. Therefore, the first step in influencing instrumentality is to connect pay and other rewards to performance using bonuses, award systems, and merit pay. However, this is not always sufficient, because people may not be aware of some of the rewards awaiting high performers. Publicizing any contests or award programs is needed to bring rewards to the awareness of employees. It is also important to highlight that performance, not something else, is being rewarded. For example, if a company has an employee of the month award that is rotated among employees, employees are unlikely to believe that performance is being rewarded. This type of meritless reward system may actually hamper the motivation of the highest performing employees by eroding instrumentality.
Influencing Valence
Employees are more likely to be motivated if they find the reward to be attractive. This process involves managers finding what their employees value. Desirable rewards tend to be fair and satisfy different employees’ diverging needs. Ensuring high valence involves getting to know a company’s employees. Talking to employees and surveying them about what rewards they find valuable are some methods to gain understanding. Finally, giving employees a choice between multiple rewards may be a good idea to increase valence.
Ways in Which Managers Can Influence Expectancy, Instrumentality, and Valence
Expectancy |
Instrumentality |
Valence |
| • Make sure employees have proper skills, abilities, and knowledge
• Ensure that the environment facilitates performance • Provide encouragement to make people believe that their effort makes a difference |
• Reward employee performance • Inform people in advance about the rewards • Try to eliminate non-performance influence over rewards |
• Find rewards that are desirable to employees • Make sure that the rewards are viewed as fair • Give employees choice over rewards |
Reinforcement Theory
Reinforcement theory is based on the work of Ivan Pavlov on behavioral conditioning and the later work of B. F. Skinner on operant conditioning (Skinner, 1953). According to reinforcement theory, behavior is a function of its outcomes. Imagine that even though no one asked you to, you stayed late and drafted a report. When the manager found out, she was ecstatic and took you out to lunch and thanked you genuinely. The consequences following your good deed were favorable, and therefore you are more likely to demonstrate similar behaviors in the future. In other words, your taking initiative was reinforced. Instead, if your manager had said nothing about it and everyone ignored the sacrifice you made, you are less likely to demonstrate similar behaviors in the future.
Reinforcement theory is based on a simple idea that may be viewed as common sense. Beginning at infancy we learn through reinforcement. If you have observed a small child discovering the environment, you will see reinforcement theory in action. When the child discovers manipulating a faucet leads to water coming out and finds this outcome pleasant, he is more likely to repeat the behavior. If he burns his hand while playing with hot water, the child is likely to stay away from the faucet in the future.
Despite the simplicity of reinforcement, how many times have you seen positive behavior ignored, or worse, negative behavior rewarded? In many organizations, this is a familiar scenario. People go above and beyond the call of duty, yet their actions are ignored or criticized. People with disruptive habits may receive no punishments because the manager is afraid of the reaction the person will give when con- fronted. Problem employees may even receive rewards such as promotions so they will be transferred to a different location and become someone else’s problem. Moreover, it is common for people to be rewarded for the wrong kind of behavior. Steven Kerr has labeled this phenomenon “the folly of rewarding A while hoping for B” (Kerr, 1995). For example, a company may make public statements about the importance of quality. Yet, if they choose to reward shipments on time regardless of the amount of defects contained in the shipments, employees are more likely to ignore quality and focus on hurrying the delivery process. Because people learn to repeat their behaviors based on the consequences following their prior activities, managers will need to systematically examine the consequences of employee behavior and make interventions when needed.
Reinforcement Interventions
Reinforcement theory describes four interventions to modify employee behavior. Two of these are methods of increasing the frequency of desired behaviors, while the remaining two are methods of reducing the frequency of undesired behaviors.
Reinforcement Methods
Positive Reinforcement |
Negative Reinforcement |
| Positive behavior followed by positive consequences (Manager praises the employee) | Positive behavior followed by removal of negative consequences (Manager stops nagging the employee) |
Punishment |
Extinction |
| Negative behavior followed by negative consequences (Manager demotes the employee) | Negative behavior followed by removal of positive consequences (Manager ignores the behavior) |
Positive reinforcement is a method of increasing the desired behavior (Beatty & Schneier, 1975). Positive reinforcement involves making sure that behavior is met with positive consequences. For example, praising an employee for treating a customer respectfully is an example of positive reinforcement. If the praise immediately follows the positive behavior, the employee will see a link between the behavior and positive consequences and will be motivated to repeat similar behaviors.
Negative reinforcement is also used to increase the desired behavior. Negative reinforcement involves removal of unpleasant outcomes once desired behavior is demonstrated. Nagging an employee to complete a report is an example of negative reinforcement. The negative stimulus in the environment will remain present until positive behavior is demonstrated. The problem with negative reinforcement is that the negative stimulus may lead to unexpected behaviors and may fail to stimulate the desired behavior. For example, the person may start avoiding the manager to avoid being nagged.
Extinction is used to decrease the frequency of negative behaviors. Extinction is the removal of rewards following negative behavior. Sometimes, negative behaviors are demonstrated because they are being inadvertently rewarded. For example, it has been shown that when people are rewarded for their unethical behaviors, they tend to demonstrate higher levels of unethical behaviors (Harvey & Sims, 1978). Thus, when the rewards following unwanted behaviors are removed, the frequency of future negative behaviors may be reduced. For example, if a coworker is forwarding unsolicited e-mail messages containing jokes, commenting and laughing at these jokes may be encouraging the person to keep forwarding these messages. Completely ignoring such messages may reduce their frequency.
Punishment is another method of reducing the frequency of undesirable behaviors. Punishment involves presenting negative consequences following unwanted behaviors. Giving an employee a warning for consistently being late to work is an example of punishment.
Reinforcement Schedules
In addition to types of reinforcements, researchers have focused their attention on schedules of reinforcement as well (Beatty & Schneier, 1975). Reinforcement is presented on a continuous schedule if reinforcers follow all instances of positive behavior. An example of a continuous schedule would be giving an employee a sales commission every time he makes a sale. In many instances, continuous schedules are impractical. For example, it would be difficult to praise an employee every time he shows up to work on time. Fixed-ratio schedules involve providing rewards every nth time the right behavior is demonstrated. An example of this would be giving the employee a bonus for every tenth sale he makes. Variable ratio involves providing the reinforcement on a random pattern, such as praising the employee occasionally when the person shows up on time. In the case of continuous schedules, behavioral change is more temporary. Once the reward is withdrawn, the person may stop performing the desired behavior. The most durable results occur under variable ratios, but there is also some evidence that continuous schedules produce higher performance than do variable schedules (Beatty & Schneier, 1975; Cherring- ton & Cerrington, 1974; Saari & Latham, 1982; Yukl & Latham, 1975).
Toolbox: Be Effective in Your Use of Discipline
As a manager, sometimes you may have to discipline an employee to eliminate unwanted behavior. Here are some tips to make this process more effective.
- Consider whether punishment is the most effective way to modify behavior. Sometimes catching people in the act of doing good things and praising or rewarding them is preferable to punishing negative behavior. Instead of criticizing them for being late, consider praising them when they are on time. Carrots may be more effective than sticks. You can also make the behavior extinct by removing any rewards that follow undesirable behavior.
- Be sure that the punishment fits the crime. If a punishment is too harsh, both the employee in question and coworkers who will learn about the punishment will feel it is unfair. Unfair punishment may not change unwanted behavior.
- Be consistent in your treatment of employees. Have disciplinary procedures and apply them in the same way to everyone. It is unfair to enforce a rule for one particular employee but then give others a free pass.
- Document the behavior in question. If an employee is going to be disciplined, the evidence must go beyond hearsay.
- Be timely with discipline. When a long period of time passes between behavior and punishment, it is less effective in reducing undesired behavior because the connection between the behavior and punishment is weaker.
Sources: Adapted from ideas in Ambrose, M. L., & Kulik, C. T. (1999). Old friends, new faces: Motivation research in the 1990s. Journal of Management, 25, 231–292; Guffey, C. J., & Helms, M. M. (2001). Effective employee discipline: A case of the Internal Revenue Service. Public Personnel Management, 30, 111–128.
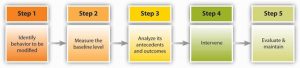
A systematic way in which reinforcement theory principles are applied is called Organizational Behavior Modification (or OB Mod) (Luthans & Stajkovic, 1999). This is a systematic application of reinforcement theory to modify employee behaviors in the workplace. The model consists of five stages. The process starts with identifying the behavior that will be modified. Let’s assume that we are interested in reducing absenteeism among employees. In step 2, we need to measure the baseline level of absenteeism. How many times a month is a particular employee absent? In step 3, the behavior’s antecedents and consequences are determined. Why is this employee absent? More importantly, what is happening when the employee is absent? If the behavior is being unintentionally rewarded (e.g., the person is still getting paid or is able to avoid unpleasant assignments because someone else is doing them), we may expect these positive consequences to reinforce the absenteeism. Instead, to reduce the frequency of absenteeism, it will be necessary to think of financial or social incentives to follow positive behavior and negative consequences to follow negative behavior. In step 4, an intervention is implemented. Removing the positive consequences of negative behavior may be an effective way of dealing with the situation, or, in persistent situations, punishments may be used. Finally, in step 5 the behavior is measured periodically and maintained.
Studies examining the effectiveness of OB Mod have been supportive of the model in general. A review of the literature found that OB Mod interventions resulted in 17% improvement in performance (Stajkovic & Luthans, 1997). Particularly in manufacturing settings, OB Mod was an effective way of increasing performance, although positive effects were observed in service organizations as well.
Source: Based on information presented in Stajkovic, A. D., & Luthans, F. (1997). A meta-analysis of the effects of organizational behavior modification on task performance, 1975–1995. Academy of Management Journal, 40, 1122–1149.
Key Takeaway
Process-based theories use the mental processes of employees as the key to understanding employee motivation. According to equity theory, employees are demotivated when they view reward distribution as unfair. Perceptions of fairness are shaped by the comparisons they make between their inputs and outcomes with respect to a referent’s inputs and outcomes. Following equity theory, research identified two other types of fairness (procedural and interactional) that also affect worker reactions and motivation. According to expectancy theory, employees are motivated when they believe that their effort will lead to high performance (expectancy), when they believe that their performance will lead to outcomes (instrumentality), and when they find the outcomes following performance to be desirable (valence). Reinforcement theory argues that behavior is a function of its consequences. By properly tying rewards to positive behaviors, eliminating rewards following negative behaviors, and punishing negative behaviors, leaders can increase the frequency of desired behaviors. These three theories are particularly useful in designing reward systems within a company.
7.4 The Role of Ethics and National Culture
Motivation and Ethics
What motivates individuals to behave unethically? Motivation theories have been applied to explain this interesting and important question. One theory that has been particularly successful in explaining ethical behavior is reinforcement theory. Just like any other behavior such as performance or cooperation, ethical behavior is one that is learned as a result of the consequences following one’s actions. For example, in an experiment simulating the job of a sales manager, participants made a series of decisions using a computer. Partway through the simulation, subjects were informed that salespeople reporting to them were giving kickbacks to customers. Subjects in this experiment were more likely to cut the kickbacks if there was a threat of punishment to the manager. On the other hand, subjects playing the sales manager were more likely to continue giving away the kickbacks if they made a profit after providing the kick- backs (Hegarty & Sims, 1978). In a separate study highlighting the importance of rewards and punishments, researchers found that the severity of expected punishment was the primary predictor of whether subjects reported inclination to behave unethically. In addition to the severity of the punishment, the perceived likelihood of punishment was also a major influence of ethical behavior (Rettig & Rawson, 1963). These findings highlight the importance of rewards and punishments for motivating unethical behaviors.
There are many organizational situations in which individuals may do unethical things but then experience positive consequences such as being awarded promotions for meeting their sales quotas. For example, in many hotels, staff members routinely receive kickbacks from restaurants or bars if they refer customers to those locations (Elliott, 2007). Similarly, sales staff rewarded with spiffs (product-specific sales incentives) may give customers advice that goes against their own personal beliefs and in this sense act unethically (Radin & Predmore, 2002). As long as unethical behavior is followed by positive con- sequences for the person in question, we would expect unethical behavior to continue. Thus, in order to minimize the occurrence of unethical behavior (and in some instances legal problems), it seems important to examine the rewards and punishments that follow unethical behavior and remove rewards following unethical behavior while increasing the severity and likelihood of punishment.
Motivation Around the Globe
Motivation is a culturally bound topic. In other words, the factors that motivate employees in different cultures may not be equivalent. The motivation theories we cover in this chapter are likely to be culturally bound because they were developed by Western researchers and the majority of the research sup- porting each theory was conducted on Western subjects.
Based on the cultural context, Maslow’s hierarchy of needs may require modification because the ranking of the needs may differ across cultures. For example, a study conducted in 39 countries showed that financial satisfaction was a stronger predictor of overall life satisfaction in developing nations compared to industrialized nations. In industrialized nations, satisfaction with esteem needs was a more powerful motivator than it was in developing nations (Oishi, Diener, & Suh, 1999).
People around the world value justice and fairness. However, what is perceived as fair may be culturally dependent. Moreover, people in different cultures may react differently to perceived unfairness (Erdogan & Liden, 2006; Mueller & Wynn, 2000). There is also some evidence indicating that equity (rewarding employees based on their contributions to a group) may be a culture-specific method of achieving fairness.
Key Takeaway
Motivation theories are particularly useful for understanding why employees behave unethically. Based on reinforcement theory, people will demonstrate higher unethical behaviors if their unethical behaviors are followed by rewards or go unpunished. Similarly, according to expectancy theory, if people believe that their unethical actions will be rewarded with desirable outcomes, they are more likely to demonstrate unethical behaviors. In terms of culture, some of the motivation theories are likely to be culture-bound, whereas others may more readily apply to other cultures. Existing research shows that what is viewed as fair or unfair tends to be culturally defined.
7.5 Motivation in Action: The Case of Trader Joe’s
People in Hawaiian T-shirts. Delicious fresh fruits and vegetables. A place where parking is tight and aisles are tiny. A place where you will be unable to find half the things on your list but will go home satisfied. We are, of course, talking about Trader Joe’s (a privately held company), a unique grocery store headquartered in California and located in 22 states. By selling store-brand and gourmet foods at affordable prices, this chain created a special niche for itself. Yet the helpful employees who stock the shelves and answer questions are definitely key to what makes this store unique and helps it achieve twice the sales of traditional supermarkets.
Shopping here is fun, and chatting with employees is a routine part of this experience. Employees are upbeat and friendly to each other and to customers. If you look lost, there is the definite offer of help. But somehow the friendliness does not seem scripted. Instead, if they see you shopping for big trays of cheese, they might casually inquire if you are having a party and then point to other selections. If they see you chasing your toddler, they are quick to tie a balloon to his wrist. When you ask them if they have any cumin, they get down on their knees to check the back of the aisle, with the attitude of helping a guest that is visiting their home. How does a company make sure its employees look like they enjoy being there to help others?
One of the keys to this puzzle is pay. Trader Joe’s sells cheap organic food, but they are not “cheap” when it comes to paying their employees. Employees, including part-timers, are among the best paid in the retail industry. Full-time employees earn an average of $40,150 in their first year and also earn average annual bonuses of $950 with $6,300 in retirement contributions. Store managers’ average compensation is $132,000.
With these generous benefits and above-market wages and salaries, the company has no difficulty attracting qualified candidates.
But money only partially explains what energizes Trader Joe’s employees. They work with people who are friendly and upbeat. The environment is collaborative, so that people fill in for each other and managers pick up the slack when the need arises, including tasks like sweeping the floors. Plus, the company promotes solely from within, making Trader Joe’s one of few places in the retail industry where employees can satisfy their career aspirations. Employees are evaluated every 3 months and receive feedback about their performance.
Employees are also given autonomy on the job. They can open a product to have the customers try it and can be honest about their feelings toward different products. They receive on- and off-the-job training and are intimately familiar with the products, which enables them to come up with ideas that are taken seriously by upper management. In short, employees love what they do, work with nice people who treat each other well, and are respected by the company. When employees are treated well, it is no wonder they treat their customers well daily.
Based on information from Lewis, L. (2005). Trader Joe’s adventure. Chicago: Dearborn Trade; McGregor, J., Salter, C., Conley, L., Haley, F., Sacks, D., & Prospero, M. (2004). Customers first. Fast Company, 87, 79–88; Speizer, I. (2004). Shopper’s special. Workforce Management, 83, 51–55.
7.6 Conclusion
In this chapter we have reviewed the basic motivation theories that have been developed to explain motivated behavior. Several theories view motivated behavior as attempts to satisfy needs. Based on this approach, managers would benefit from understanding what people need so that the actions of employees can be understood and managed. Other theories explain motivated behavior using the cognitive processes of employees. Employees respond to unfairness in their environment, they learn from the con- sequences of their actions and repeat the behaviors that lead to positive results, and they are motivated to exert effort if they see their actions will lead to outcomes that would get them desired rewards. None of these theories are complete on their own, but each theory provides us with a framework we can use to analyze, interpret, and manage employee behaviors in the workplace.
Adapted from: Chapter 5 of Organizational Behavior
[Author removed at request of original publisher]
UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA LIBRARIES PUBLISHING EDITION, 2017. THIS EDITION ADAPTED FROM A WORK ORIGINALLY PRODUCED IN 2010 BY A PUBLISHER WHO HAS REQUESTED THAT IT NOT RECEIVE ATTRIBUTION. MINNEAPOLIS, MN
![]()

