Chapter 3: Training and Development
Training and Development
Training: Not Like It Used to Be
Imagine this: You have a pile of work on your desk and as you get started, your Outlook calendar reminds you about a sexual harassment training in ten minutes. You groan to yourself, not looking forward to sitting in a conference room and seeing PowerPoint slide after PowerPoint slide. As you walk to the conference room, you run into a colleague who is taking the same training that day and commiserate on how boring this training is probably going to be. When you step into the conference room, however, you see something very different.
Computers are set up at every chair with a video ready to start on the computer. The HR manager greets you and asks you to take a seat. When the training starts, you are introduced (via video) on each of the computers to a series of sexual harassment example scenarios. The videos stop, and there is a recorded discussion about what the videos portrayed. Your colleagues in the Washington, DC, office are able to see the same training and, via video conferencing, are able to participate in the discussions. It is highly interactive and interesting. Once the training is finished, there are assignments to be completed via specific channels that have been set up for this training. You communicate about the material and complete the assignments in teams with members of your Washington, DC, office. If you want to review the material, you simply click on a review and the entire session or parts of the training can be reviewed. In fact, on your bus ride home from work, you access the channels on your iPhone, chatting with a colleague in your other office about the sexual harassment training assignment you have due next week. You receive an e-mail from your HR manager asking you to complete a training assessment located in a specific channel in the software, and you happily comply because you have an entirely new perspective on what training can be.
This is the training of today. No longer do people sit in hot, stuffy rooms to get training on boring content. Training has become highly interactive, technical, and interesting owing to the amount of multimedia we can use. Sun Microsystems, for example, has developed just the kind of software mentioned above, called Social Learning eXchange (SLX). This type of training allows people across the country to connect with each other, saving both money and time. In fact, Sun Microsystems received a Best Practices Award from Training Magazine for this innovative software in 2010[1]. The SLX software allows training to be delivered in an interactive manner in multiple locations. The implications of this type of software are numerous. For example, SLX is used at Sun Professional Services division by delivering instructional videos on tools and software, which employees can view at their own pace[2]. There is also a channel in the software that allows the vice president to communicate with employees on a regular basis to improve employee communications. In another example, this software can be used to quickly communicate product changes to the sales team, who then begin the process of positioning their products to consumers. Training videos, including breakout sessions, can save companies money by not requiring travel to a session. These can even be accessed using application technology on cell phones. Employees can obtain the training they need in the comfort of their own city, office, or home. Someone is sick the day the training is delivered? No problem; they can review the recorded training sessions.
An estimated $1,400 per employee is spent on training annually, with training costs consuming 2.72 percent of the total payroll budget[3] for the average company. With such a large amount of funds at stake, HR managers must develop the right training programs to meet the needs; otherwise, these funds are virtually wasted. This chapter is all about how to assess, develop, implement, and measure an effective training program.
3.1 Steps to Take in Training an Employee
Any effective company has training in place to make sure employees can perform his or her job. During the recruitment and selection process, the right person should be hired to begin with. But even the right person may need training in how your company does things. Lack of training can result in lost productivity, lost customers, and poor relationships between employees and managers. It can also result in dissatisfaction, which means retention problems and high turnover. All these end up being direct costs to the organization. In fact, a study performed by the American Society for Training and Development (ASTD) found that 41 percent of employees at companies with poor training planned to leave within the year, but in companies with excellent training, only 12 percent planned to leave (Branham, 2005). To reduce some costs associated with not training or undertraining, development of training programs can help with some of the risk. This is what this chapter will address.
For effective employee training, there are four steps that generally occur. First, the new employee goes through an orientation, and then he or she will receive in-house training on job-specific areas. Next, the employee should be assigned a mentor, and then, as comfort with the job duties grows, he or she may engage in external training. Employee training and development is the process of helping employees develop their personal and organization skills, knowledge, and abilities.
Employee Orientation
The first step in training is an employee orientation. Employee orientation is the process used for welcoming a new employee into the organization. The importance of employee orientation is two-fold. First, the goal is for employees to gain an understanding of the company policies and learn how their specific job fits into the big picture. Employee orientation usually involves filling out employee paperwork such as I-9 and 401(k) program forms.
The goals of an orientation are as follows:
- To reduce start-up costs. If an orientation is done right, it can help get the employee up to speed on various policies and procedures, so the employee can start working right away. It can also be a way to ensure all hiring paperwork is filled out correctly, so the employee is paid on time.
- To reduce anxiety. Starting a new job can be stressful. One goal of an orientation is to reduce the stress and anxiety people feel when going into an unknown situation.
- To reduce employee turnover. Employee turnover tends to be higher when employees don’t feel valued or are not given the tools to perform. An employee orientation can show that the organization values the employee and provides tools necessary for a successful entry.
- To save time for the supervisor and coworkers. A well-done orientation makes for a better prepared employee, which means less time having to teach the employee.
- To set expectations and attitudes. If employees know from the start what the expectations are, they tend to perform better. Likewise, if employees learn the values and attitudes of the organization from the beginning, there is a higher chance of a successful tenure at the company.
Some companies use employee orientation as a way to introduce employees not only to the company policies and procedures but also to the staff. For an example of an orientation schedule for the day, see below:
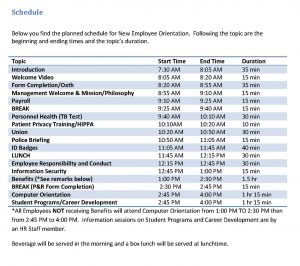
Source: Sample schedule courtesy of Louis Stokes Cleveland VA Medical Center, (accessed September 2, 2011).
In-House Training
In-house training programs are learning opportunities developed by the organization in which they are used. This is usually the second step in the training process and often is ongoing. In-house training programs can be training related to a specific job, such as how to use a particular kind of software. In a manufacturing setting, in- house training might include an employee learning how to use a particular kind of machinery.
Many companies provide in-house training on various HR topics as well, meaning it doesn’t always have to relate to a specific job. Some examples of in-house training include the following:
- Ethics training
- Sexual harassment training
- Multicultural training
- Communication training
- Management training
- Customer service training
- Operation of special equipment
- Training to do the job itself
- Basic skills training
As you can tell by the list of topics, HR might sometimes create and deliver this training, but often a supervisor or manager delivers the training.
Mentoring
After the employee has completed orientation and in-house training, companies see the value in offering mentoring opportunities as the next step in training. Sometimes a mentor may be assigned during in-house training. A mentor is a trusted, experienced advisor who has direct investment in the development of an employee. A mentor may be a supervisor, but often a mentor is a colleague who has the experience and personality to help guide someone through processes. While mentoring may occur informally, a mentorship program can help ensure the new employee not only feels welcomed but is paired up with someone who already knows the ropes and can help guide the new employee through any on-the-job challenges.
To work effectively, a mentoring program should become part of the company culture; in other words, new mentors should receive in-house training to be a mentor. Mentors are selected based on experience, willingness, and personality. IBM’s Integrated Supply Chain Division, for example, has successfully implemented a mentorship program. The company’s division boasts 19,000 employees and half of IBM’s revenues, making management of a mentorship program challenging. However, potential mentors are trained and put into a database where new employees can search attributes and strengths of mentors and choose the person who closely meets their needs. Then the mentor and mentee work together in development of the new employee. “We view this as a best practice,” says Patricia Lewis-Burton, vice president of human resources, Integrated Supply Chain Division. “We view it as something that is not left to human resources alone. In fact, the program is imbedded in the way our group does business” (Witt, 2005).
Some companies use short-term mentorship programs because they find employees training other employees to be valuable for all involved. Starbucks, for example, utilizes this approach. When it opens a new store in a new market, a team of experienced store managers and baristas are sent from existing stores to the new stores to lead the store-opening efforts, including training of new employees.
External Training
External training includes any type of training that is not performed in-house. This is usually the last step in training, and it can be ongoing. It can include sending an employee to a seminar to help further develop leadership skills or helping pay tuition for an employee who wants to take a marketing class. To be a Ford automotive technician, for example, you must attend the Ford ASSET Program, which is a partnership between Ford Motor Company, Ford dealers, and select technical schools1.
How Would You Handle This?
To Train or Not to Train
Towanda Michaels is the human resource manager at a medium-size pet supply wholesaler. Casey Cleps is a salesperson at the organization and an invaluable member of the team. Last year, his sales brought in about 20 percent of the company revenue alone. Everybody likes Casey: he is friendly, competent, and professional.
Training is an important part of the company, and an e-mail was sent last month that said if employees do not complete the required safety training by July 1, they would be let go.
It is July 15, and it has just come to Towanda’s attention that Casey has not completed the online safety training that is required for his job. When she approaches him about it, he says, “I am the best salesperson here; I can’t waste time doing training. I already know all the safety rules anyway.”
Questions to Ponder
Would you let Casey go, as stated in the e-mail? How would you handle this?
Key Takeaways: 3.1 Steps to Take in Training an Employee
3.2 Types of Training
There are a number of different types of training we can use to engage an employee. These types are usually used in all steps in a training process (orientation, in-house, mentorship, and external training). The training utilized depends on the amount of resources available for training, the type of company, and the priority the company places on training. Companies such as The Cheesecake Factory, a family restaurant, make training a high priority. The company spends an average of $2,000 per hourly employee. This includes everyone from the dishwasher and managers to the servers. For The Cheesecake Factory, this expenditure has paid off. They measure the effectiveness of its training by looking at turnover, which is 15 percent below the industry average (Ruiz, 2006). Servers make up 40 percent of the workforce and spend two weeks training to obtain certification. Thirty days later, they receive follow-up classes, and when the menu changes, they receive additional training (Ruiz, 2006). Let’s take a look at some of the training we can offer our employees.
As you will see from the types of training below, no one type would be enough for the jobs we do. Most HR managers use a variety of these types of training to develop a holistic employee.
Technical or Technology Training
Depending on the type of job, technical training will be required. Technical training is a type of training meant to teach the new employee the technological aspects of the job. In a retail environment, technical training might include teaching someone how to use the computer system to ring up customers. In a sales position, it might include showing someone how to use the customer relationship management (CRM) system to find new prospects. In a consulting business, technical training might be used so the consultant knows how to use the system to input the number of hours that should be charged to a client. In a restaurant, the server needs to be trained on how to use the system to process orders. Let’s assume your company has decided to switch to the newest version of Microsoft Office. This might require some technical training of the entire company to ensure everyone uses the technology effectively. Technical training is often performed in-house, but it can also be administered externally.
Quality Training
In a production-focused business, quality training is extremely important. Quality training refers to familiarizing employees with the means of preventing, detecting, and eliminating nonquality items, usually in an organization that produces a product. In a world where quality can set your business apart from competitors, this type of training provides employees with the knowledge to recognize products that are not up to quality standards and teaches them what to do in this scenario. Numerous organizations, such as the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), measure quality based on a number of metrics. This organization provides the stamp of quality approval for companies producing tangible products. ISO has developed quality standards for almost every field imaginable, not only considering product quality but also certifying companies in environmental management quality. ISO9000 is the set of standards for quality management, while ISO14000 is the set of standards for environmental management. ISO has developed 18,000 standards over the last 60 years1. With the increase in globalization, these international quality standards are more important than ever for business development. Some companies, like 3M (QAI, 2011), choose to offer ISO training as external online training, employing companies such as QAI to deliver the training both online and in classrooms to employees.
Training employees on quality standards, including ISO standards, can give them a competitive advantage. It can result in cost savings in production as well as provide an edge in marketing of the quality-controlled products. Some quality training can happen in-house, but organizations such as ISO also perform external training.
Skills Training
Skills training, the third type of training, includes proficiencies needed to actually perform the job. For example, an administrative assistant might be trained in how to answer the phone, while a salesperson at Best Buy might be trained in assessment of customer needs and on how to offer the customer information to make a buying decision. Think of skills training as the things you actually need to know to perform your job. A cashier needs to know not only the technology to ring someone up but what to do if something is priced wrong. Most of the time, skills training is given in-house and can include the use of a mentor. An example of a type of skills training is from AT&T and Apple (Whitney, 2011), who in summer 2011 asked their managers to accelerate retail employee training on the iPhone 5, which was released to market in the fall.
Soft Skills Training
Our fourth type of training is called soft skills training. Soft skills refer to personality traits, social graces, communication, and personal habits that are used to characterize relationships with other people. Soft skills might include how to answer the phone or how to be friendly and welcoming to customers. It could include sexual harassment training and ethics training. In some jobs, necessary soft skills might include how to motivate others, maintain small talk, and establish rapport. In a retail or restaurant environment, soft skills are used in every interaction with customers and are a key component of the customer experience. In fact, according to a Computerworld magazine survey, executives say there is an increasing need for people who have not only the skills and technical skills to do a job but also the necessary soft skills, such as strong listening and communication abilities (Hoffman, 2007). Many problems in organizations are due to a lack of soft skills, or interpersonal skills, not by problems with the business itself. As a result, HR and managers should work together to strengthen these employee skills. Soft skills training can be administered either in-house or externally.
Professional Training and Legal Training
In some jobs, professional training must be done on an ongoing basis. Professional training is a type of training required to be up to date in one’s own professional field. For example, tax laws change often, and as a result, an accountant for H&R Block must receive yearly professional training on new tax codes (Silkey, 2010). Lawyers need professional training as laws change. A personal fitness trainer will undergo yearly certifications to stay up to date in new fitness and nutrition information.
Some organizations have paid a high cost for not properly training their employees on the laws relating to their industry. In 2011, Massachusetts General Hospital paid over $1 million in fines related to privacy policies that were not followed (Donnelly, 2011). As a result, the organization has agreed to develop training for workers on medical privacy. The fines could have been prevented if the organization had provided the proper training to begin with. Other types of legal training might include sexual harassment law training and discrimination law training.
Team Training
Do you know the exercise in which a person is asked to close his or her eyes and fall back, and then supposedly the team members will catch that person? As a team-building exercise (and a scary one at that), this is an example of team training. The goal of team training is to develop cohesiveness among team members, allowing them to get to know each other and facilitate relationship building. We can define team training as a process that empowers teams to improve decision making, problem solving, and team-development skills to achieve business results. Often this type of training can occur after an organization has been restructured and new people are working together or perhaps after a merger or acquisition. Some reasons for team training include the following:
- Improving communication
- Making the workplace more enjoyable
- Motivating a team
- Getting to know each other
- Getting everyone “onto the same page,” including goal setting
- Teaching the team self-regulation strategies
- Helping participants to learn more about themselves (strengths and weaknesses)
- Identifying and utilizing the strengths of team members
- Improving team productivity
- Practicing effective collaboration with team members
Team training can be administered either in-house or externally. Ironically, through the use of technology, team training no longer requires people to even be in the same room.
Managerial Training
After someone has spent time with an organization, they might be identified as a candidate for promotion. When this occurs, managerial training would occur. Topics might include those from our soft skills section, such as how to motivate and delegate, while others may be technical in nature. For example, if management uses a particular computer system for scheduling, the manager candidate might be technically trained. Some managerial training might be performed in-house while other training, such as leadership skills, might be performed externally.
For example, Mastek, a global IT solutions and services provider, provides a program called “One Skill a Month,” which enables managers to learn skills such as delegation, coaching, and giving feedback. The average number of total training days at Mastek is 7.8 per employee2 and includes managerial topics and soft skills topics such as e-mail etiquette. The goal of its training programs is to increase productivity, one of the organization’s core values.
Safety Training
Safety training is a type of training that occurs to ensure employees are protected from injuries caused by work-related accidents. Safety training is especially important for organizations that use chemicals or other types of hazardous materials in their production. Safety training can also include evacuation plans, fire drills, and workplace violence procedures. Safety training can also include the following:
- Eye safety
- First aid
- Food service safety
- Hearing protection
- Asbestos
- Construction safety
- Hazmat safety
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration, or OSHA, is the main federal agency charged with enforcement of safety and health regulation in the United States. OSHA provides external training to companies on OSHA standards. Sometimes in-house training will also cover safety training.
On-the-Job Coaching Training Delivery
On-the-job coaching is one way to facilitate employee skills training. On-the-job coaching refers to an approved person training an employee on the skills necessary to complete tasks. A manager or someone with experience shows the employee how to perform the actual job. The selection of an on-the-job coach can be done in a variety of ways, but usually the coach is selected based on personality, skills, and knowledge. This type of skills training is normally facilitated in-house. The disadvantage of this training revolves around the person delivering the training. If he or she is not a good communicator, the training may not work. Likewise, if this person has “other things to do,” he or she may not spend as much time required to train the person and provide guidance. In this situation, training can frustrate the new employee and may result in turnover.
Mentoring and Coaching Training Delivery
Mentoring is also a type of training delivery. A mentor is a trusted, experienced advisor who has direct investment in the development of an employee. Mentoring is a process by which an employee can be trained and developed by an experienced person. Normally, mentoring is used as a continuing method to train and develop an employee. One disadvantage of this type of training is possible communication style and personality conflict. It can also create overdependence in the mentee or micromanagement by the mentor. This is more different than on-the-job coaching, which tends to be short term and focuses on the skills needed to perform a particular job.
Brown Bag Lunch Training Delivery
Brown bag lunches are a training delivery method meant to create an informal atmosphere. As the name suggests, brown bag lunch training is one in which the training occurs during lunchtime, employees bring their food, and someone presents training information to them. The trainer could be HR or management or even another employee showing a new technical skill. Brown bag lunches can also be an effective way to perform team training, as it brings people together in a more relaxed atmosphere. Some companies offer brown bag lunch training for personal development as well. For example, HR might want to bring in a specialist on 401(k) plans, or perhaps an employee provides a slide presentation on a trip he or she has taken, discussing the things learned on the trip. One disadvantage to this type of training can be low attendance and garnering enough interest from employees who may not want to “work” during lunch breaks. There can also be inconsistency in messages if training is delivered and not everyone is present to hear the message.
Web-Based Training Delivery
Web-based training delivery has a number of names. It could be called e-learning or Internet-based, computer- based, or technology-based learning. No matter what it is called, any web-based training involves the use of technology to facilitate training. There are two types of web-based learning. First, synchronous learning uses instructor-led facilitation. Asynchronous learning is self-directed, and there is no instructor facilitating the course. There are several advantages to web-based training. First, it is available on demand, does not require travel, and can be cost efficient. However, disadvantages might include an impersonal aspect to the training and limited bandwidth or technology capabilities1.
Web-based training delivery lends itself well to certain training topics. For example, this might be an appropriate delivery method for safety training, technical training, quality training, and professional training. However, for some training, such as soft-skills training, job skills training, managerial training, and team training, another more personalized method may be better for delivery. However, there are many different platforms that lend themselves to an interactive approach to training, such as Sun Microsystems’ Social Learning eXchange (SLX) training system, which has real-time video and recording capabilities. Hundreds of platforms are available to facilitate web-based training. DigitalChalk, for example, allows for both synchronous and asynchronous training and allows the instructor or human relations manager to track training progress and completion (DigitalChalk, 2010). Some companies use SharePoint, an intranet platform, to store training videos and materials (Microsoft SharePoint, 2010). Blackboard and Angel (used primarily by higher education institutions) allows human resource managers to create training modules, which can be moderated by a facilitator or managed in a self-paced format. In any of the platforms available, media such as video and podcasts can be included within the training.
Considerations for selecting a web-based platform include the following:
- Is there a one-time fee or a per-user fee?
- Do the majority of your employees use a Mac or a PC, and how does the platform work with both systems?
- Is there enough bandwidth in your organization to support this type of platform?
- Is the platform flexible enough to meet your training needs?
- Does the software allow for collaboration and multimedia?
- Is there training for the trainer in adoption of this system? Is technical support offered?
Job Shadowing Training Delivery
Job shadowing is a training delivery method that places an employee who already has the skills with another employee who wants to develop those skills. Apprenticeships use job shadowing as one type of training method. For example, an apprentice electrician would shadow and watch the journeyman electrician perform the skills and tasks and learn by watching. Eventually, the apprentice would be able to learn the skills to do the job alone. The downside to this type of training is the possibility that the person job shadowing may learn “bad habits” or shortcuts to performing tasks that may not be beneficial to the organization.
Fortune 500 Focus
It takes a lot of training for the Walt Disney Company to produce the best Mickey Mouse, Snow White, Aladdin, or Peter Pan. In Orlando at Disneyworld, most of this training takes place at Disney University. Disney University provides training to its 42,000 cast members (this is what Disney calls employees) in areas such as culinary arts, computer applications, and specific job components. Once hired, all cast members go through a two-day Disney training program called Traditions, where they learn the basics of being a good cast member and the history of the company. For all practical purposes, Traditions is a new employee orientation.
Training doesn’t stop at orientation, though. While all positions receive extensive training, one of the most extensive trainings are especially for Disney characters, since their presence at the theme parks is a major part of the customer experience. To become a character cast member, a character performer audition is required. The auditions require dancing and acting, and once hired, the individual is given the job of several characters to play. After a two-week intensive training process on character history, personalities, and ability to sign the names of the characters (for the autograph books sold at the parks for kids), an exam is given. The exam tests competency in character understanding, and passing the exam is required to become hired (Hill, 2005).
While Disney University trains people for specific positions, it also offers an array of continuing development courses called Disney Development Connection. Disney says in 2010, more than 3,254,596 hours were spent training a variety of employees2, from characters to management. The training doesn’t stop at in-house training, either. Disney offers tuition reimbursement up to $700 per credit and pays for 100 percent of books and $100 per course for cost of other materials. In 2010, Disney paid over $8 million in tuition expenses for cast members2. Disney consistently ranks in “America’s Most Admired Companies” by Fortune Magazine, and its excellent training could be one of the many reasons.
Job Swapping Training Delivery
Job swapping is a method for training in which two employees agree to change jobs for a period of time. Of course, with this training delivery method, other training would be necessary to ensure the employee learns the skills needed to perform the skills of the new job. Job swap options can be motivational to employees by providing a change of scenery. It can be great for the organization as well to cross-train employees in different types of jobs. However, the time spent learning can result in unproductive time and lost revenue.
Vestibule Training Delivery
In vestibule training, training is performed near the worksite in conference rooms, lecture rooms, and classrooms. This might be an appropriate method to deliver orientations and some skills-based training. For example, to become a journeyman electrician, an apprentice performs job shadowing, on-the-job training, and vestibule training to learn the law and codes related to electricity installation. During the busy holiday season, Macy’s uses vestibule training to teach new hires how to use the cash register system and provides skills training on how to provide great customer service (Macy’s, 2010).
Many organizations use vestibule training for technical training, safety training, professional training, and quality training. It can also be appropriate for managerial training, soft skills training, and team training. As you can tell, this delivery method, like web-based training delivery, is quite versatile. For some jobs or training topics, this may take too much time away from performing the actual “job,” which can result in lost productivity.
International Assignment Training
Since we are working within a global economy, it might be necessary to provide training to employees who are moving overseas or working overseas. Up to 40 percent of international assignments are terminated early because of a lack of international training (Sullivan & Tu, 2011). Ensuring success overseas is reliant upon the local employee’s learning how to navigate in the new country. The following topics might be included in this type of training:
- Cultural differences and similarities
- Insight and daily living in the country
- Social norms and etiquette
- Communication training, such as language skills
This training is best delivered by a professional in the region or area in which the employee will be working.
- Training delivery methods are important to consider, depending on the type of training that needs to be performed.
- Most organizations do not use only one type of training delivery method; a combination of many methods will be used.
- On-the-job coaching delivery method is a training delivery method in which an employee is assigned to a more experienced employee or manager to learn the skills needed for the job. This is similar to the mentor training delivery method, except a mentor training method is less about skills training and more about ongoing employee development.
- Brown bag lunch training delivery is normally informal and can involve personal development as well as specific job-related skills.
- Web-based training is any type of training that is delivered using technology.
- There are numerous platforms that can be used for web-based training and considerations, such as cost, when selecting a platform for use.
- A synchronous training method is used for web-based training and refers to delivery that is led by a facilitator. An asynchronous training method is one that is self-directed.
- Job shadowing is a delivery method consisting of on-the-job training and the employee’s learning skills by watching someone more experienced.
- To motivate employees and allow them to develop new skills, job swapping training delivery may be used. This occurs when two people change jobs for a set period of time to learn new skills. With this method, it is likely that other methods will also be used, too.
- Vestibule training delivery is also known as “near site” training. It normally happens in a classroom, conference room, or lecture room and works well to deliver orientations and some skills-based training. Many organizations also use vestibule training for technical training, safety training, professional training, and quality training.
- Since many companies operate overseas, providing training to those employees with international assignments can better prepare them for living and working abroad.
Adapted from Chapter 8 of University of Minnesota (2016) Human Resource Management, Open Textbook Library. ![]()
1“2010 Top 25 Winners,” Training Magazine, accessed July 25, 2010, http://www.trainingmag.com/article/ 2010-top-125-winners.
2“Video Community for the Enterprise,” Social Learning eXchange, accessed July 25, 2010, http://www.slideshare.net/sociallearningexchange/social-learning-exchange-slx?from=share_email.
3See the American Society for Training and Development Trend Review, ASTD Website, accessed July 25, 2010, http://www.astd.org/.

